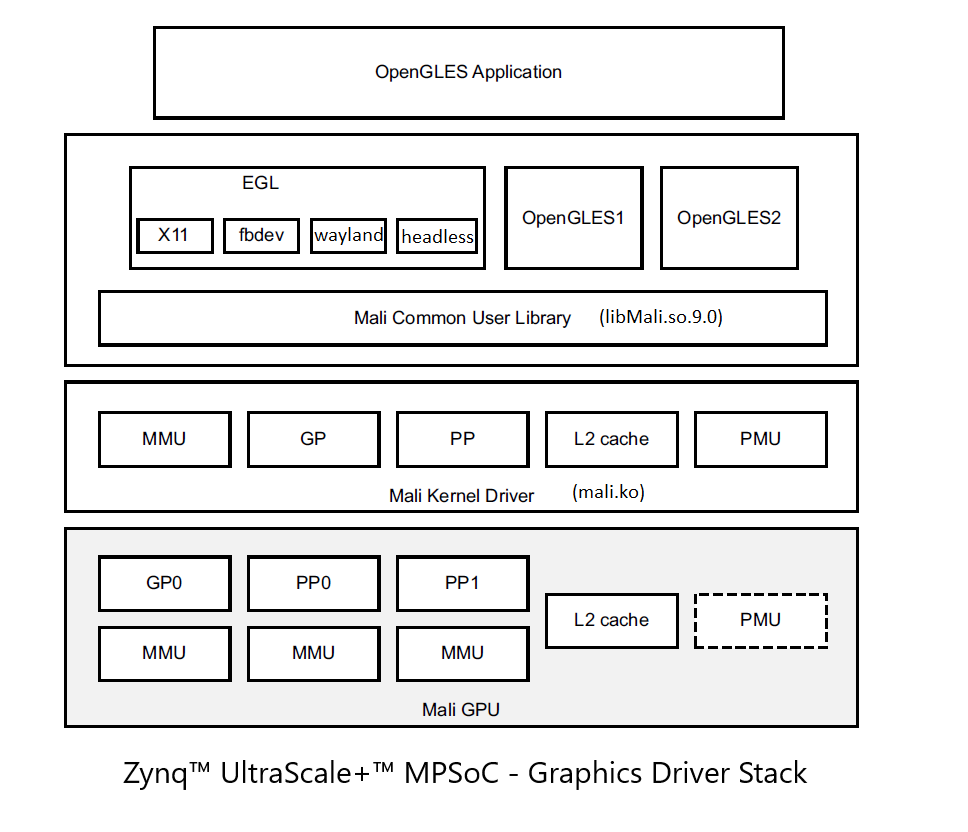
Zynq™ UltraScale+™ MPSoC - Graphics Driver Stack - Mali 400
The purpose of this page is to describe how the ARM MALI driver is integrated into Zynq™ UltraScale+™ MPSoC
Table of Contents
Overview
Zynq™ UltraScale+™ MPSoC has the MALI 400MP GPU from ARM. The ARM MALI 400MP is an OpenGLES 2.0 capable GPU.Driver access and license
The driver for MALI 400MP consists of Linux kernel driver and user library. The user space library is proprietary licensed and will have to be distributed as binaries. The user space library will be provided through AMD's PetaLinux release. The Linux kernel driver is GPL licensed, and downloadable from http://malideveloper.arm.com/. Until 2016.4, the kernel driver was hosted on github. From 2017.1, the kernel driver hosted on github is deprecated. This will now be downloaded from ARM website and packaged into the PetaLinux BSP.Note: From 2019.2 onwards the user-space binaries in the lounge are not hosted. Customers can download from https://github.com/Xilinx/mali-userspace-binaries with appropriate branch.
The driver is released periodically by ARM. Thus there can be multiple versions available. The default version in Kconfig points to the latest working release.
Device tree binding
The DT binding documentation is included in the driver release. Download the kernel driver tarball from http://malideveloper.arm.com/., unzip it and the DT binding documentation is available at the folder path."driver/documentation/devicetree/bindings/arm/mali-utgard.txt"
Runtime power management
The MALI driver supports fine grained runtime power management based on Linux runtime PM APIs, with its own scheduler. This section describes the flow of specific driver version, r7p0-00rel0, to give an overview.First the driver implements the Linux runtime PM callbacks (in mali_kernel_linux.c), and the runtime pm is enabled in device initialization (arm.c)
static const struct dev_pm_ops mali_dev_pm_ops = {
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_RUNTIME
.runtime_suspend = mali_driver_runtime_suspend,
.runtime_resume = mali_driver_runtime_resume,
.runtime_idle = mali_driver_runtime_idle,
#endif
.suspend = mali_driver_suspend_scheduler,
.resume = mali_driver_resume_scheduler,
.freeze = mali_driver_suspend_scheduler,
.thaw = mali_driver_resume_scheduler,
.poweroff = mali_driver_suspend_scheduler,
};
#endif
mali_platform_device_register()
{
...
pm_runtime_set_autosuspend_delay(&&(mali_gpu_device.dev), 1000);
pm_runtime_use_autosuspend(&&(mali_gpu_device.dev));
#endif
pm_runtime_enable(&&(mali_gpu_device.dev));
...
}
Then, the driver has its own scheduler (mali_scheduler.c) that tracks any activities of all GPU processors (GP: geometry processor, PP: pixel processor). All activities on those processors are created as a job (ex, gp job / pp job) and scheduled through this scheduler. The scheduler tracks the completion of the job as well. Based on the status, the scheduler sets the runtime pm reference count accordingly (mali_scheduler.c). Below is an example for GP. Equivalent functions exist for PP.
mali_scheduler_queue_gp_job()
{
...
_mali_osk_pm_dev_ref_get_async()
...
}
mali_scheduler_complete_gp_job()
{
...
_mali_osk_pm_dev_ref_pet_async()
...
}
When the reference count reaches to 0, the runtime_suspend callback will be triggered: runtime_suspend callback -> mali_driver_runtime_suspend() -> mali_pm_runtime_suspend() -> mali_pm_common_suspend(). mali_pm_common_suspend() performs a series of operations to put all relevant modules, ex, l2 cache and mmu, in idle state. Reverse operations is performed when resuming.
mali_pm_common_suspend()
{
...
if (0 < num_groups_down) {
mali_executor_group_power_down(groups_down, num_groups_down);
}
for (i = 0; i < num_l2_down; i++) {
mali_l2_cache_power_down(l2_down[i]);
}
...
}
GPU software stack
Changelog
- 2023.1
- Fix for compatibility with 6.1 Linux kernel
- Updated clock name to match LIMA driver
- Added attribute support for weston
- Performance Issues with Weston 10+ in 2023.1. So below is AR for downgrading weston to 9.0.0
- 2021.1
- Update EGL headers
- Fix for compatibility with 5.10 Linux kernel
Selecting particular backends:
You can select particular backend while configuring rootfs
File: project-spec/config/rootfs_config
petalinux-config -c rootfs
- Wayland/GBM backend:
By default, plnx build system will try to package all the backends in the rootfs and depending upon the rootfs config, we create a link to the correct backend. Fbdev, X11, wayland and headless are the choices we have.
For example: Once you have selected libmali through 'petalinux-config -c rootfs', select backend to wayland and unselect 'packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox' and 'packagegroup-petalinux-x11' and select 'packagegroup-petalinux-weston'. After selection your rootfs_config will look as below.
CONFIG_libmali-xlnx=y CONFIG_mali-backend-wayland=y
This packagegroup ensures all the essential wayland/weston packages are packaged into the rootfs for having a wayland/weston application work out of the box. On boot, export following parameter in your terminal console.
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/
Now, you can run sample benchmarking application glmark2-es2-wayland.
- X11 backend:
By default, Mali supports X11 backend. Just select libmali-xlnx package from 'petalinux-config -c rootfs'. The root filesystem should now have libmali with X11 support. Also, please select at least one window manager. For example: packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox.
Once you have selected libmali through 'petalinux-config -c rootfs', and selected backend to x11, your rootfs_config will look as below.
CONFIG_libmali-xlnx=y CONFIG_mali-backend-x11=y
- Fbdev backend:
Just select libmali-xlnx package from 'petalinux-config -c rootfs' and select fbdev backend.
Once you have selected libmali through 'petalinux-config -c rootfs' unselect 'packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox' and 'packagegroup-petalinux-x11'. Your rootfs_config will look as below.
CONFIG_libmali-xlnx=y CONFIG_mali-backend-fbdev=y
- Headless-EGL backend:
Just select libmali-xlnx package from 'petalinux-config -c rootfs' and select headless backend. Unselect 'packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox' and 'packagegroup-petalinux-x11'.
Once you have selected libmali through 'petalinux-config -c rootfs', and selected backend to headless, your rootfs_config will look as below.
CONFIG_libmali-xlnx=y CONFIG_mali-backend-headless=y
Please find more details for Headless rendering on below page.
Mali 400 Headless rendering
Benchmark:
To run a benchmark example for x11 and wayland backend, please add below lines to build/conf/local.conf
IMAGE_INSTALL:append = "glmark2"
Update-alternatives:
You should have all backends packaged in the rootfs and you can switch between multiple backends using update-alternatives commands as follows:
To Update a link:
update-alternatives --install /usr/lib/libMali.so.9.0 libmali /usr/lib/fbdev/libMali.so.9.0 90
To remove a link:
update-alternatives --remove libmali /usr/lib/libMali.so.9.0
For more info, perform update-alternatives --help
Alternate solution: Users can always modify links using "ln" commands
Running GPU applications:
Create project
source settings.sh petalinux-create -t project -s xilinx-zcu106-v2023.1-final.bsp
Setting Petalinux BSP configuration
File: project-spec/meta-user/conf/petalinuxbsp.conf
For generating rootfs for compiling application or any libraries add below configs
EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES = "debug-tweaks dev-pkgs"
Enabling and disabling rootfs configs
petalinux-config -c rootfs
For enabling qt application for any backend
CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-qt=y
- x11
CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox=y
CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-x11=y - fbdev
# CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox is not set
# CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-x11 is not set - wayland
CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-weston=y
# CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox is not set
# CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-x11 is not set - headless backend
CONFIG_libmali-xlnx=y
CONFIG_mali-backend-headless=y
# CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-x11 is not set
# CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-matchbox is not set
Building project
petalinux-build
Running applications
- GLMARK2 application
- x11 backend
Run Xorg application in backend or start xserver service if not running
Xorg -depth 16 & systemctl start xserver-nodm
Run glmark application
export DISPLAY=:0.0 glmark2-es2
- wayland backend
Start weston if not running
systemctl start weston
Run glmark application
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/ glmark2-es2-wayland
- x11 backend
QT applications
- x11 backend (Xorg should be running or xserver-nodm service should be started)
Run Xorg or xserver service
/usr/bin/Xorg -depth 16 & (if Xorg or xserver-nodm service is not running) or systemctl start xserver-nodm
Set environment variables
export DISPLAY=:0.0 export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=eglfs export QT_QPA_EGLFS_WIDTH=1920 export QT_QPA_EGLFS_HEIGHT=1080 export QT_QPA_GENERIC_PLUGINS=evdevmouse,evdevkeyboard export QT_QPA_ENABLE_TERMINAL_KEYBOARD=1 export QT_QPA_FONTDIR=/usr/share/fonts/truetype export QT_QPA_PLATFORM_PLUGIN_PATH=/usr/lib/qt5/plugins export QML2_IMPORT_PATH=/usr/lib/qt5/qml
Run example (eg: analogclock)
cd /usr/share/examples/gui/analogclock/ ./analogclock
- fbdev backend (Disable any Xorg or weston if running)
Set environment variables
export DISPLAY=:0.0 export QT_QPA_EGLFS_INTEGRATION=eglfs_mali export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=eglfs::fb=/dev/fb0 export QT_QPA_EGLFS_FB=/dev/fb0 export QT_QPA_EGLFS_WIDTH=1920 export QT_QPA_EGLFS_HEIGHT=1080 export QT_QPA_GENERIC_PLUGINS=evdevmouse,evdevkeyboard export QT_QPA_ENABLE_TERMINAL_KEYBOARD=1 export QT_QPA_FONTDIR=/usr/share/fonts/truetype export QT_QPA_PLATFORM_PLUGIN_PATH=/usr/lib/qt5/plugins export QML2_IMPORT_PATH=/usr/lib/qt5/qml
Run application (eg: dockwidget)
cd /usr/share/examples/widgets/mainwindows/dockwidgets ./dockwidgets
wayland backend (weston should be running)
- x11 backend (Xorg should be running or xserver-nodm service should be started)
If weston is not running, enable weston service
systemctl start weston
Set environment variables
export DISPLAY=:0.0 export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/ export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=wayland export QT_WAYLAND_SHELL_INTEGRATION=xdg-shell (for >2023.1 release) export QT_WAYLAND_SHELL_INTEGRATION=wl-shell (till 2022.2 and older releases)
Run applications
cd /usr/share/examples/widgets/widgets/sliders/ ./sliders cd /usr/share/examples/gui/analogclock/ ./analogclock cd /usr/share/examples/widgets/mainwindows/dockwidgets/ ./dockwidgets
Enabling LIMA for 2023.1
- Add next line to the project-spec/meta-user/conf/petalinuxbsp.conf:
- DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED += "libmali"
- Applications ran:
- x11:
- vivid_tex, glmark2-es2, glcts, QT applications
- fbdev:
- eglfbdev, eglfbdev_gears, QT applications
- wayland:
- glmark2-es2-wayland, glcts, QT applications
- x11:
- Limitations:
- x11:
- All x11 applications are failing with segmentation fault while running.
- fbdev:
- Application compilation issues for eglfbdev and eglfbdev_gears
- wayland:
- glcts application compilation issues
- x11:
Related Links
- Xilinx Arm Mali-400 Driver Archive
- Linux Drivers
- Adding MALI userpace binaries in Yocto builds
- Zynq UltraScale+MPSoC Graphics- GPU application debugging using ARM Mali Graphics Debugger tool
- Zynq UltraScale+MPSoC Graphics- GPU Profiling using ARM Streamline performance analyzer
- Mali 400 optimization guide
- Xilinx ARM MALI 400 Support
- MALI developers
Related content
© Copyright 2019 - 2022 Xilinx Inc. Privacy Policy