Macb Driver
Paths, files, links and documentation on this page are given relative to the Linux kernel source tree.
Table of Contents
HW IP features
- Speed support for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- MAC loopback and PHY loopback
- Partial store and forward option
- Packet buffer option
- Flow control - TX/RX pause
- Checksum offload support, CRC checking, FCS stripping
- Promiscuous mode, Broadcast mode
- Collision detection and enforcement - this is an IP feature, no SW support required
- MDIO support for PHY layer management
- Multicasting support
- VLAN tagged frames
- Half duplex support
- Programmable IPG
- External FIFO interface
- Wake on LAN
- IEEE1588 support for ZynqMP and Versal
- Jumbo frame size support for ZynqMP and Versal
- 64 bit addressing for ZynqMP and Versal
- Priority queue support for ZynqMP and Versal
- PS SGMII support (hardwired to 1Gbps) is present in ZynqMP
Features supported in driver
(Functional HW IP and stack related features)- Speed support for 10/100/1000 Mbps with clock framework
- Packet buffer option
- Checksum offload support, CRC checking, FCS stripping
- MDIO support for PHY layer management
- Multicasting support
- Programmable IPG
- IEEE1588 support for ZynqMP and Versal
- Jumbo frame size support for ZynqMP and Versal
- 64 bit addressing for ZynqMP and Versal
- Priority queue support for ZynqMP and Versal
- PS SGMII support is present in ZynqMP and supported in the driver
- This driver can be used with PL SGMII/1000BaseX driver on Zynq, ZynqMP and Versal
- This driver can be used with gmii2rgmii converter driver
- Support for EthTool queries
- RX NAPI support
- Clock adaptation on Zynq, ZynqMP and Versal
- Runtime PM and suspend/resume supported on ZynqMP and Versal
- Partial store and forward
- Wake on LAN support using ARP on ZynqMP and Versal
- Dynamic SGMII configuration support on Xilinx Zynq Ultrascale+MPSoC
Missing Features, Known Issues and Limitations
- Linux does not support loopback
- Flow control support is not present in the driver. RX pause frames can be received by the IP but TX pause frame support is not provided.
- External FIFO interface is not supported by the driver - this implementation is DMA based.
- No interrupt support for PHY events in driver. The current implementation relies on polling method for phy event
- No IEEE 1588 support for Zynq-7000 as the timestamp implementation in IP is not accurate enough.
- The timestamp generated on a PTP event is stored in a non-latching register. This means that the timestamp is overwritten whenever a PTP event packet arrives. Hence there is no foolproof way to associate a timestamp with the packet.
- An application using sync, follow up, pdelay request, pdelay response with a sync cycle of 1 second and NO errors in between might possibly work but it is not reliable because sync will fail the moment there is any deviation: i.e. multiple back to back PTP event packets in the same direction (or) a small sync interval on a high traffic system where the SW is unable to process the timestamp register before it is overwritten.
- WOL does not work on warm restart designs because GEM WOL requires an RX BD scratch area that is accessible even during suspend (OCM is used for this) and OCM is secure in this design which is a limitation for this feature.
- A warning "unable to generate target frequency" is displayed during macb boot during multiple conditions. Please note the following scenarios and the validity of the warning:
- Clock source is from internal PLL with GEM in RGMII mode: warning is valid; please check your HW design and Devicetree clock entries
- Clock source is external and user defined: warning can be ignored as this clock is not controlled by CCF; but to avoid the warning, please ensure that the Devicetree clock entry for tx_clk points to a fixed clock node with the frequency that you are supplying
- Clock source is from an internal GT (applicable on ZU+ in SGMII mode only): warning can be ignored as the GT clock is already fixed at 125MHz; CCF has no provision to acquire this information or control this clock and hence this warning is displayed
Important AR links
- WOL does not work on warm restart designs due to some limitations (2018.1/2/3) - AR-71028
- PTP time adjustment for a large negative delta fails in 2018.1/2 - AR-71332
- MACB MDIO bus support - Please find the patches for 2017.1, 2017.2, 2017.3, 2017.4, 2018.1, 2018.2 and 2018.3 at the AR - AR-69132
- ZynqMP PS SGMII GT initialization and related - AR-68866
- ZynqMP PS SGMII fixed link - AR-69769 (apllicable till 2021.2 release)
- TI PHY design on ZynqMP evaluation board has incorrect straps and can be remedied with a SW workaround (already implemented in drivers) - AR-70686
- PL PCS PMA initialization in fsbl for Zynq and ZynqMP - refer to xapp1026 and xapp130
- For custom Versal designs using AIE on 2020.1, make sure the low DDR region is accessible to LPD slaves (including GEM) using a workaround.
- There is a performance drop of ~100Mbps between 2020.1 (5.4 Linux kernel) and 2019.2 (4.19 Linux kernel) observed on both GEM and Axi Ethernet on Zynq. This is currently suspected to be the result of change in the net framework and there is no workaround yet. Further updates will be documented in AR-75195
- Macb + PL PCS PMA ifconfig down/up may fail without proper reset and clock reinitialization. Please refer to AR-72806.
- Timestamping issue in gPTP master mode (applicable only for 2022.2/2023.1) - AR-000035307
- For full list of ARs, search XKB
Kernel Configuration
The following config options should be enabled in order to build the macb driverCONFIG_ETHERNET
CONFIG_MACB
CONFIG_NETDEVICES
CONFIG_HAS_DMA
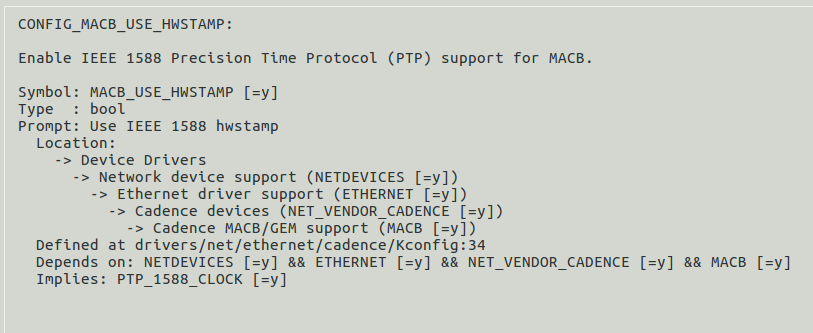
CONFIG_MACB_USE_HWSTAMP
Use IEEE 1588 hwstamp (only supported in ZynqMP and Versal) - This config option supports use of 1588 HW TSTAMP support in ZynqMP & Versal and depends on MACB.
This option enables IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) support for MACB.
Devicetree
Compatible string can be:- "xlnx,zynq-gem" for Zynq-7000
- "xlnx,zynqmp-gem" for ZynqMP. This compatible string enables use of jumbo frame sizes, 1588 and HW timestamping suport and any features exclusive to ZynqMP.
- "xlnx,versal-gem" for Versal. This compatible string enables use of jumbo frame sizes, 1588 and HW timestamping suport, automatic flow control, 802.1AS and any features exclusive to Versal.
Note: Compatible string of format "cdnx,XXXX" is deprecated.
For more details on phy bindings please refer "Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/cdns,macb.yaml" (macb.txt in older version)
gem0: ethernet@e000b000 {
compatible = "cdns,gem";
reg = <0xe000b000 0x1000>;
status = "disabled";
interrupt-parent = <&gic>;
interrupts = <0 22 4>;
clocks = <&clkc 30>, <&clkc 30>, <&clkc 13>;
clock-names = "pclk", "hclk", "tx_clk";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
phy-handle = <ðernet_phy>;
phy-mode = "rgmii-id";
ethernet_phy: ethernet-phy@7{
reg = <7>;
};
};
Related devicetree information
Ethernet DT
For generic ethernet DT property information, refer to:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/ethernet-controller.yaml
PHY DT
For PHY related DT information, refer to:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/ethernet-phy.yamlWhen selecting phy specific settings, make sure to mention interface type, speed (if limited/fixed) and phy address properties.
DO NOT set compatible strings in ethernet PHY nodes. Ethernet phy devices are recognized based on identifier registers and phy address; it is not recommended to use compatible string.
Xilinx converter and PHY DT
PHY/Converter devices that may be used with this MAC:
- Xilinx GMII2RGMII converter (https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/xlnx%2Cgmii-to-rgmii.yaml)
- Xilinx PCS PMA PHY ( https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/xilinx-phy.txt )
RGMII Tuning in DT
RGMII tuning is driven in phy framework using "rgmii-id", "rgmii-txid", "rgmii-rxid" properties Make sure to set phy-mode to any of these as per your board requirement.
In addition to enabling tuning, some phys also give control of tuning values via devicetree. Please refer to the devicetree bindings documentation of the phy you use in order to tune these according to your board.
TSU clock in DT
Clock adaption is present by default for all device families. For more details refer to devicetree clock bindings and respective wiki pages.
ZynqMP and Versal also have tsu-clk adaption support in addition to all the other reference clocks.
Fixed link DT
This driver can be used for a MAC - MAC fixed link connection. In order to do so, please update the devicetree fixed link node as per
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/ethernet-controller.yaml#L158
Common MDIO DT
To use multiple GEM→PHY connections using a common MDIO bus, please use the following devicetree convention:
gem0 {
......
phy-handle = <&phya>;
mdio {
phya {
reg = <0xa>;
};
phyb {
reg = <0xb>;
};
};
};
gem1 {
.....
phy-handle = <&phyb>;
};
Where:
→ gem0 is the instance whose phy management is being used (and whose MDC and MDI lines are connected to both PHYs)
→ gem0 is communicating via phya and gem1 is communicating via phyb
Note: For versions upto 2022.1, gem0 needs to come up before gem1 and stay up (because the MDIO interface is expected to be up first; otherwise, the dependent MAC-PHY link (gem1-phyb) will come up on next ifconfig up/down).
As a result of this gem0's runtime PM will not be effective if gem1 is still active in this configuration.
For versions starting 2022.2, probe order and PM suspend/resume order is automatically handled in the driver based on MDIO producer and consumer.
PS SGMII DTs (ZynqMP only)
→ The DT node for PS SGMII is the same as any other configuration with phy-mode property set to "sgmii" and a phy node as seen below. In this case, the Linux SW(currently phylib, NOT phylink) ensures autonegotiation is performed with the PHY. In addition, PCS block inside of GEM will also negotiate and provide link status information in PCS_status register (to be read twice because of stick bits).
gem0 {
......
phy-mode = <sgmii>;
phy-handle = <&phya>;
phya {
reg = <0xa>;
};
};
→ If there is no MDIO access to the SGMII PHY or if SFPs are used, then the phy-mode should be set to sgmii and fixed link node should be used instead of phy node. PCS autoneg will be disabled and PCS_status register will always report link up (to be read twice because of sticky bits). This solution is available in releases 2022.1 and above. For previous releases, please refer to "Important AR links"
Pointers on PHY reset via GPIO
→ For boards which require a PHY reset via GPIO, please see the generic framework provisions here: https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/ethernet-phy.yaml#L141
This can be used for multiple PHYs with independent GPIO resets as well.
→ If reset is required before PHY detection, please see the MDIO bus provision here: https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/mdio.yaml#L30
→ When using PHY reset via GPIO, please check manufacturer specific datasheet for the reset polarity, reset assert duration and post de-assert delay for PHY to be functional. These values can then be passed to PHY and MDIO framework via Devicetree documentation above.
Performance
These benchmark performance numbers were obtained by connecting Xilinx boards to Linux PCs/server machines (Ubuntu/Red Hat Enterprise).The tool used is netperf (Refer to tool information below).
The protocol, MTU size and option to note CPU load can all be selected from netperf/netserver options
Zynq
Board: ZC706CPU Freq: 666MHz (A9)
Link Speed: 1000Mbps, Full duplex
Linux version: 6.1
| TCP (Mbps) | UDP(Mbps) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTU | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) |
| 1500 | 728.76 | 97.29 | 548.70 | 95.96 | 565.6 | 65.00 | 444.8 | 99.55 |
Linux version: 5.4 and above
NOTE- There is ~10% drop in performance (compared to 2019.2) for 1500 MTU.
The drop is due to this commit enabling CONFIG_OPTIMIZE_INLINING forcibly in linux kernel. It is observed on GEM and Xilinx Axi Ethernet drivers on Zynq.
Kernel and networking stack has a large number of inline functions and it could be some unoptimized inline function (could also be dependent on gcc version) leading to performance drop.
The plan is to document this performance drop on Zynq and initiate a discussion with mainline community so that it is analyzed by respective kernel maintainers.
| TCP (Mbps) | UDP(Mbps) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTU | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) |
| 1500 | 654.79 | 93.11 | 737.63 | 81.43 | 486.8 | 63.56 | 303 | 96.23 |
Linux version: 5.10
| TCP (Mbps) | UDP(Mbps) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTU | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) |
| 1500 | 675.79 | 90.68 | 759.22 | 86.45 | 455.0 | 62.95 | 690.1 | 82.99 |
ZynqMP
Board: ZCU102CPU Freq 1100MHz (A53)
Link Speed 1000Mbps, Full duplex
DDR 533MHz
CCU: No
Linux version: 6.6
| TCP (Mbps) | UDP (Mbps) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTU | TX | CPU (%) | RX | CPU (%) | TX | CPU (%) | RX | CPU (%) |
| 1500 | 941.37 | 5.0 | 930.64 | 54.94 | 957.0 | 20.3 | 961.6 | 22.07 |
| 8192 | 988.95 | 2.34 | 989.07 | 7.94 | 991.9 | 5.80 | 992.0 | 5.54 |
Test Procedure
Diagnostic and Protocol Tests
PING
This utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol(IP) network and to measure the round trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer.How to run:
ping <Remote IP Address>
WebServer
Connect zynq board to a Linux x86 machine. Ensure that telnet server is running on the Zynq board. It tests for remote access for Zynq board on host machineOpen a web browser on host machine and enter the static IP assigned to zynq board. Webpage is expected to be displayed properly.
Telnet
telnet <Server IP Address>
FTP & TFTP
How to run:Open a ftp client on the host with the Zynq.
x86> ftp 192.168.1.10
x86> mput <file_name>
Pkt Generator
Please refer to link below for how to run and various optionshttps://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/pktgen.txt
Performance Tests
Netperf
How to run:Server:
netserver
taskset 2 ./netperf -H <Server IP> -t TCP_STREAM taskset 2 ./netperf -H <Server IP> -t UDP_STREAM
http://www.netperf.org/netperf/
Iperf
How to run:Server:
./iperf_arm -s -u ./iperf_arm -s
./iperf_arm -c <Server IP> -u -b <banwidth> ./iperf_arm -c <Server IP>
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iperf
Stress Test
Iperf with option -d
Run iperf in dual testing mode. This will cause the server to connect back to the client on the port specified in the -L option (or defaults to the port the client connected to the server on). This is done immediately therefore running the tests simultaneously../iperf_arm -c <Server IP> -d
Ping flood test
Users can send hundred or more packets per second using -f option. It prints a ‘.’ when a packet is sent, and a backspace is printed when a packet is receivedping -f localhost
PTP
1588 synchronization can be tested on ZynqMP and Versal using open source linuxptp application.http://linuxptp.sourceforge.net/
The setup requires a master with precise clock and timstamping capabilities, typically a NIC or another 1588 capable device.
How to run
master:
#ptp4l -i <interface name> -m
#ptp4l -i <interface name> -s -m
Mainline status
The macb driver is currently at mainline kernel 6.1 with some patches pulled in from later kernels. The patches that not yet in any mainline kernel are as follows:- WOL via ARP support (~70 lines)
- Partial store and forward support (~80 lines) - in upstream 6.5 kernel
- Minor differences around PCS PMA handling
PHY details
The following PHYs were tested with ZynqMP GEM:- TI DP83867IR
- TI DP83867E (SGMII)
- Marvell 88E1112
- Marvell 88E1510/2
- Realtek RTL8211
- Vitesse VSC8211
- Micrel KSZ9031
- VSC8531_02
Change Log
2024.1
Summary:
- Upgrade to 6.6 kernel
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2024.1/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2023.2
Summary:
- Bugfixes from mainline to support pclk>160MHz and to fix PTP Timestamp failure due to packet padding
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2023.2/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2023.1
Summary:
- Fixes for macb SGMII wake source configuration
- Upgrade to 6.1 mainline version including minor updates around napi weight removal, macb phy PM support
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2023.1/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2022.2
Summary:
- Macb common MDIO bus enhancements in initialization and suspend/resume flows including SGMII phy handling.
- Fixes on ethtool WOL helper and inclusion of macb pad and fcs support for fragmented packets.
- PTP fixes on one step sync support and to add PTP TX timestamps for all packets in alignment with HWTSTAMP_TX_ON definition.
- Mainline fixes for TX restart handling under TXUBR conditions, compatible string prefix (deprecation of cdns to use xlnx)
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2022.2/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2022.1
Summary:
- Align with mainline 5.15 driver to use phylink and PCS functionality.
- Add support for (Internal) SGMII Dynamic Configuration support on Zynq Ultrascale+ MPSoC
- Minor bugfixes including fix for possible rotting packet in RX queue due to NAPI ordering.
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2022.1/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2021.2
No Changes
2021.1
Summary:
- New updates from 5.10 including phylink support.
- Minor bugfixes including DMA & coherent DMA mask handling, error handling for WOL ARP etc.
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2021.1/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2020.2
Summary:
- Minor bugfix for high memory DMA handling.
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2020.2/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2020.1
Summary:
- Minor bug fixes including
- Workaround for TSO IP errata on Versal GEM.
- Handle PHY reset for IPs such as PCS PMA phy.
- Increase halt timeout to accommodate 10Mbps.
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2020.1/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2019.2
Summary:
- Minor feature updates
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2019.2.01/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
2019.1
Summary:
- Bug fixes and enhancements on top of 4.19 kernel
Commits:
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/commits/xilinx-v2019.1/drivers/net/ethernet/cadence
acbe29b net: macb: Apply RXUBR workaround only to versions with errata
7caaf8e net: macb: Fix napi calls in macb_suspend/resume
235128d net: macb: Fix merge error in capabilities in config struct
fee8215 net: macb: Remove repeated tasklet init
95977dd net: macb: Remove unused variables
41f029d net: macb: Remove repeated RBQP assignment
7193098 net: macb: Disable macb pad and fcs for fragmented packets
7d069bc net: macb: Sync RXUBR changes with mainline
d77376c Revert "net: macb: Do not call PM sync in mdio helpers"
d8dd5fe Revert "net: macb: Remove pm calls in mdio timeout function"
f5520f1 macb: Sync PHY reset with mainline
e5c7c2e net: macb: Add separate definition for PPM fraction
24e1145 net: macb: Fix SUBNS increment and increase resolution
b10faf3 net: macb: Optimize reading HW timestamp
e393646 net: macb: Add NULL check for PCLK and HCLK
f22dab1 net: macb: Sync macb_config usage with mainline
9c71c6e net: macb: Change interrupt and napi enable order in open
> 4.19 Mainline fixes pulled in:
af3a961 net: ethernet: cadence: fix socket buffer corruption problem
65f81f2 net: macb: remove unnecessary code
ea79ec6 net: macb: restart tx after tx used bit read
aef9308 net: macb: fix random memory corruption on RX with 64-bit DMA
6b28540 net: macb: fix dropped RX frames due to a race
db8102b net: macb: Check for SKBTX_HW_TSTAMP in macb driver
2018.3
Summary:
- Bug fixes and minor enhancements
Commits:
9caf0ef net: macb: Fix BUG unregistering invalid mdiobus
86bbb72 net: macb: Use devicetree phy-handle if available
41bc0b5 net: macb: Fix warning about uninitialized phy_node
1e7f173 net: macb: Initialize bool to false instead of zero
c5316f6 net: macb: Remove redundant ptp clock selection
0eddb82 macb: refactor the duplicate code to use a shared function
7b2d994 macb: Do not check for timeout when PHY is idle
c241cc8 net: macb: Fix ptp time adjustment for large negative delta
43c7d00 net: macb: Increment rx bd head after allocating skb and buffer
835b617 net: macb: Process tx timestamp only on ptp packets
d2b7486 net: macb: Do not call PM sync in mdio helpers
f4eb775 net: macb: Fix phy path in macb resume
7b7c156 net: macb: Remove pm calls in mdio timeout function
No changes
2018.1
Summary:
- Use mainline implementation of 64 bit addressing
- Use mainline implementation of PTP support
- Add clock management for tsu-clk
- Add WOL support for ZynqMP
Sync with 4.14 mainline kernel
9aa7608 net: macb: Add tsu_clk property and use it
e964800 net: macb: Add WOL support for ZynqMP
53ec68b net: macb: Fix GEM crash when suspend/resume plus down/up is done
2d522a5 net: macb: Remove older MACB_EXT_BD config option
617ea48 net: macb: Correct check for 64 bit addressing
fa19565 net: macb: Add phy suspend and resume
95a33ee net: macb: Set rx mode in resume
d7aa0c8 net: macb: Update macb RX tie-off descriptors
e6fca01 net: macb: Remove unnecessary DBW read back from NWCFG
23d6b42 net: macb: Cleanup empty lines
2017.4
No changes
2017.3
Summary:
- Added support for partial store and forward
- Pulled in minor mainline fixes and phy related issues
- Added support for macb suspend/resume
bf85fd4 net: macb: Add support for partial store and forward
f646336 net: macb: Fix gpio for phy reset
a29aa21 net: macb: Fix issues with FPD off
e1a214d net: macb: Misc cleanup
2017.2
Summary:
- Pulled in a minor mainline fix for mdio bus scan error check
4356634 macb: fix mdiobus_scan() error check
2017.1
Summary:
- Added PM runtime support
- Added context loss support; Cleanup around clock and suspend, resume paths. Although this support is added in macb driver, there is a know issue at the moment that GEM does not work on resume directly. It is required to bring the interface down and up again.
- Fixed ptp time adjustment for large negative delta
- Fix PHY reset and only call GPIOD functions when valid GPIO is present
- Fixed spinlocks in macb_close around ptp_clock_unregister to avoid kernel panic.
- Fixed TSU CAPS mask
- DP83867: Added a SW workaround for link instability on ZCU102 board.
afeaf15 arm64: zynqmp: macb: release spinlock before calling ptp_clock_unregister
36f7baa net: macb: Correct TSU_CAPS mask
27f1c64 macb: fix PHY reset
7613445 net: macb: Only call GPIO functions if there is a valid GPIO
2288919 net: macb: Fix ptp time adjustment for large negative delta
6cbc5cd net: cadence: macb: Fix kernel-doc format
ddd4804 net: macb: fix the clk enable and disable
1b0a659 net: macb: Add runtime support
4dc7d77 net: macb: Add context loss support
b9a2910 net: macb: Fix the double disable of clocks
756de54 net: macb: Cleanup the clock code
2f2bb37 net: macb: Fix unused warning
911b158 net: macb: Enable clocks for the mdio accesses
25f7255 net: macb: Convert the infinite wait loop to a timeout
53ac032 net: macb: Move to runtime_put to cut clocks
d415d56 net: macb: Update the phy write sequence
DP83867 phy driver:
7557928 net: macb: SW workaround for link instability on DP83867
2016.4
Summary:
- Added support for fixed link
59e3534 net: macb: Add support for fixed link
2016.3
Summary:
- Added support for 64 bit addressing
- Added support to use gmii2rgmii converter driver
- Handle HRESP error with SW reset and re-initialization of necessary parameters
- The above changes are also in mainline
b0fbcba net: macb: Handle HRESP error
ff73646 net: macb: Fixed mixed declaration and code warnings
190b6af net: macb: Update TX and RX EXT BD registers only when required
d470dfb net: macb: Correct CAPS masks
6121d00 net: macb: Add support for 64 bit addressing
f9c43e8 net: macb: add support for mdio phy nodes
Related Links
© Copyright 2019 - 2022 Xilinx Inc. Privacy Policy