Xilinx ALSA Audio I2S driver
The purpose of this page is to describe the Linux ALSA SoC driver for I2S Rx/Tx SoftIP.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Xilinx® LogiCORE™ IP I2S Transmitter and Receiver cores are soft Xilinx IP core for use with the Xilinx Vivado® Design Suite. These IPs provide easy way of sending/receiving PCM audio over I2S interface and IPs provide an easy way to interface I2S based audio DAC/ADC. These IPs requires minimal register programming. Further, the IPs support any audio sampling rates.
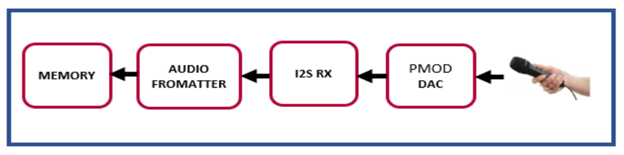
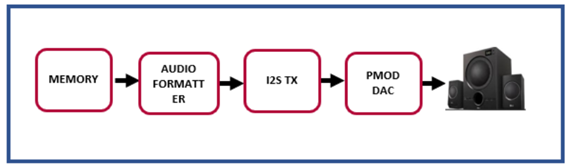
Typical system using I2S Rx and I2S Tx:
Following design depicts the typical audio I2S IP interfaces for audio recording and playback.In the following design, External I2S DAC(PMOD consisting of 3.5mm Jack) receives the data from audio source and transfers to I2S Rx where audio data is padded with AES header.On the other hand, I2STx IP removes AES header and renders PCM data through external DAC (PMOD with 3.5mm jack) to play audio on Speaker. Design uses audio formatter IP to send data from I2S to Memory and vice-versa.
The I2S Rx/Tx driver is based on the ALSA framework(refer ASoC sound card). This driver registers one of the 'component' expected by the ALSA framework. This component is responsible for configuring the I2S core to generate proper LR clock and bit clock acting as master to connected codec. This I2S driver along with audio formatter and sound card drivers will create an I2S audio pipeline. This driver cannot be used as standalone.
The driver is available at https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/sound/soc/xilinx/xlnx_i2s.c
IP/Driver Features
| IP Features | 2019.1 |
|---|---|
| Supports up to 4 I2S channels/8 audio channels | Supports only 2 channels |
| AXI4-Stream compliant | Yes |
Supports 16- and 24-bit depths. | Yes |
| Drivers is developed considering mclk fixed to 18.43MHz | Yes |
Known Issues & Limitations in Driver
- Driver doesn't need FIFO Data Count.
- Tested only 2 channel audio.
- Sampling rates tested for capture are 48 and 96kHz.
- Sampling rates tested for playback are 48, 96 and 192kHz.
Kernel Configuration
Below driver configs should be enabled.
CONFIG_SND_SOC=y CONFIG_SND_SOC_XILINX_I2S=y
Device Tree Binding
The dts node should be defined with correct hardware configuration. How to define the node is documented in xlnx,i2s.txt
Test procedure
The driver has been tested using following tools:
- ALSA Utilities.
- Gstreamer Utilities.
Note:
- Below examples assume sound card registered is #0, playback device is #0, record device is #1.
- Input audio stream properties to be recorded are sampling rate of 48000 Hz, 24 bits per sample, 2 channels.
Procedure to test I2S with ALSA utilities
Recording a file: arecord tool is used to record the audio file.
arecord -Dhw:0,1 -fS24_LE -r 48000 -c 2 -d 30 -t raw file.raw
Playing a file: aplay tool is used to play the audio file.
aplay -D hw:0,0 -fS24_LE -r 48000 -c 2 -d 30 -t raw file.raw
Device enumeration:
For record device:
arecord --device="hw:0,1" --dump-hw-params
For playback device:
aplay --device="hw:0,0" --dump-hw-params
Procedure to test I2S with Gstreamer utilities
Recording a file: gst-launch is used to record the audio file.
Gst-launch is using alsa src plugin to enable recording on i2s driver.
gst-launch-1.0 alsasrc device=hw:1,1 ! queue ! audio/x-raw,format=S24_32LE,rate=48000,channnels=2 ! filesink location=48000.raw
Playing a file: gst-launch is used to record the audio file.
Gst-launch is using alsa sink plugin to enable recording on i2s driver.
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=48000.raw ! audio/x-raw,format=S24_32LE,rate=48000,channnels=2 ! alsasink device=hw:0,0
Procedure to test I2S Pass-Through
G-streamer and alsa-utils tools enables pass through design for the i2s Linux driver i.e i2s receiver is connecting to i2s transmitter. Below is the alsa command.
arecord -D hw:0,1 -f S24_LE -r 48000 -c 2 -t raw | aplay -D hw:0,0 -c 2 -f S24_LE -r 48000 -t raw
Boards Supported
Driver has been tested on the following boards.
- ZCU106 Rev 1.0
Mainline Status
This driver is upstreamed and present at, https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/sound/soc/xilinx/xlnx_i2s.c.
Change log
2024.1
- Summary
- No changes
2020.2
- Summary
- No changes
2020.1
- Summary
- No changes
2019.2
- Summary
- No change
2019.1
- Summary:
- Used Common Clock Framework (CCF) for I2S clock configurations.
- Changed I2S driver data.
- Synced with mainlined version
- Commits:
2018.3
- Summary
- Initial release
Related Links
© Copyright 2019 - 2022 Xilinx Inc. Privacy Policy