Zynq-7000 AP SoC SATA part 2 – Ready to Run Design Example Benchmarking
Zynq-7000 AP SoC SATA part 2 – Ready to Run Design Example Benchmarking
ZYNQ-SSE- Benchmarks for the Avnet Mini-ITX
Table of Contents
The best way to contact MLE is to fill out the Contact Request Form at
>http://MLEcorp.com/ZynqSSE
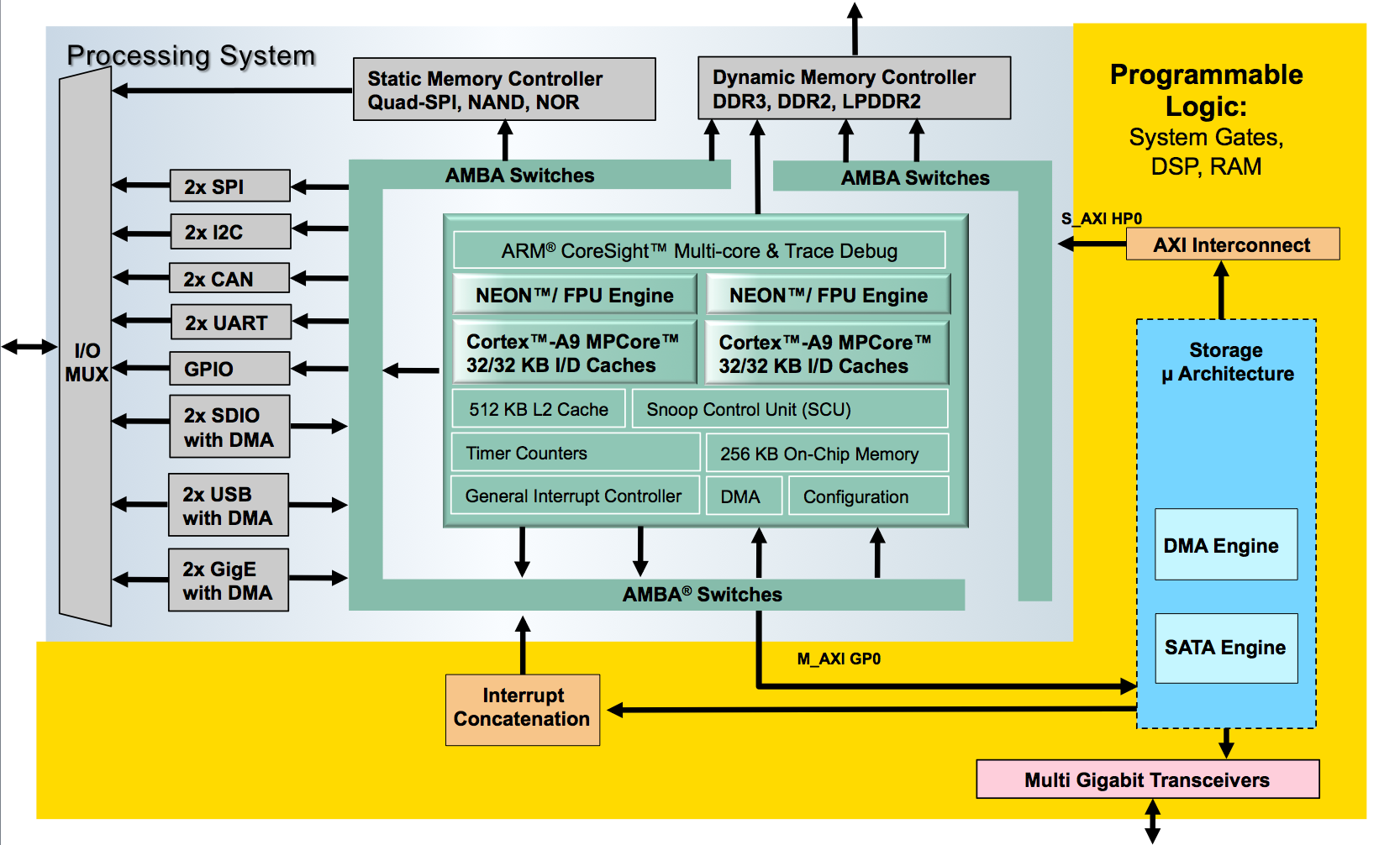
Block Diagram
The block diagram shown below gives an overview over the Zynq SSE reference design: Within the Zynq Programmable Logic (PL) the MLE storage micro-architecture instantiates the DMA and the SATA Host Controller IP blocks. The storage micro-architecture itself interfaces with the Zynq Processing System (PS) via the high-performance AXI HP0 slave port. The ARM A9 in the PS runs Xilinx PetaLinux and the SATA Linux kernel driver.Implementation
| Implementation Details | |
| Design Type | PS + PL |
| SW Type | Linux (Petalinux) |
| CPUs | 2 CPUs 700 MHz |
| PS Features | DDR, USB, UART, ETHERNET |
| PL Cores | ASICS.WS SATA IP |
| Boards/Tools | Avnet Mini ITX Z045 |
| Xilinx Tools Version | Vivado 2014.1, PETALINUX 2013-2 |
| Other Details | SATA SSD(including Cable and Power Supply), SD-Card |
| Address Map | |||
| Base Address | Size | Interface | |
| SATA IP | 0x41000000 | 4K | S AXI |
| DMA IP | 0x41010000 | 4K | S AXI, M AXI |
| Files Provided | |
| BOOT.bin | Compilation of Bitstream, FSBL and U-Boot |
| Image.ub | Linux Ramdisk Image |
MLE’s Zynq SATA Storage Extension (Zynq SSE) is a fully integrated and pre-validated system stack comprising 3rd-party SATA Host Controller and DMA IP cores from ASICS World Services, a storage micro-architecture from MLE, Xilinx PetaLinux, and an Open Source SATA Host Controller Linux kernel driver, also from MLE. Zynq SSE utilizes the Xilinx GTX Multi Gigabit Transceivers to deliver SATA I (1.5 Gbps), SATA II (3.0 Gbps), or SATA III (6 Gbps) connectivity.
The Zynq SSE is delivered as a complete reference design for the Xilinx Zynq-7000 SoC (Zynq), and effectively extends Zynq with one single SATA host port for HDD and SSD storage connectivity.
This Technical Tip shows the Benchmark results you will see after correctly setting up the system as shown in the techtip: Zynq SATA Storage Extension.
Step by Step instructions
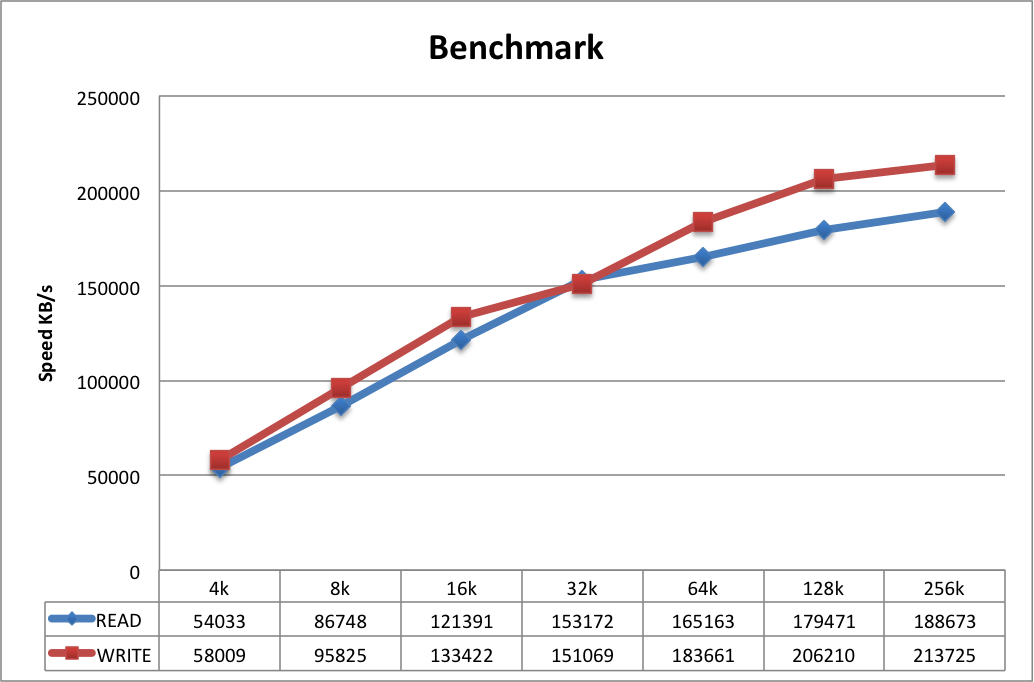
In front of Benchmarking the System, the Tech Tip “Zynq- Sata Storage Tech Tip” should be executed to have a working system. For Benchmarking the System, a tool called FIO is used. FIO is a tool that will spawn a number of threads or processes doing a particular type of I/O action as specified by the user. The typical use of FIO is to write a job file matching the I/O load one wants to simulate. We will now execute FIO with different Block sizes to see the impact on the Read and Write speeds of the system. Apply the following commands to the running SATA system, varying the Block size by using different values from 4k to 16M.Read:
fio -ioengine=sync -direct=1 -rw=read -runtime=10 -filename=/dev/sda -size=1g -name=job1 -numjobs=4 -bs=4k
fio -ioengine=sync -direct=1 -rw=write -runtime=10 -filename=/dev/sda -size=1g -name=job1 -numjobs=4 -bs=4k
Expected Results
Figure 1: Benchmark on a -2 FPGA at 700 MHZ CPU speed
© Copyright 2019 - 2022 Xilinx Inc. Privacy Policy