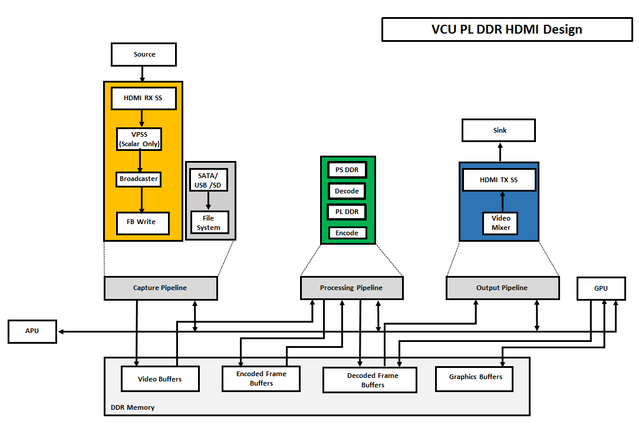
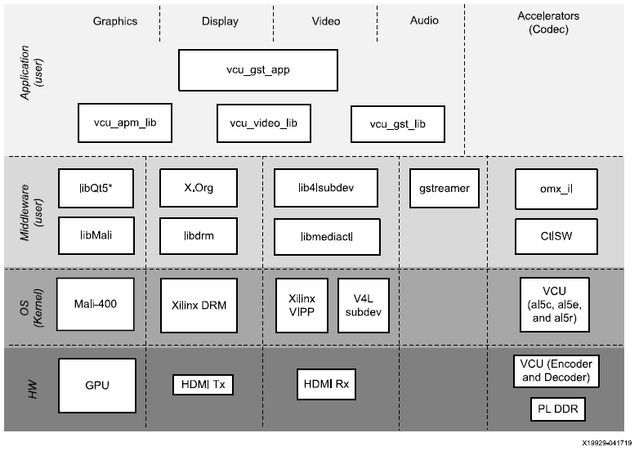
Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC VCU TRD 2019.1 - HDMI Video Capture and Display with PL DDR
Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC VCU TRD 2019.1 - HDMI Video Capture and Display with PL DDR
Table of Contents
1 Overview
This is the new design approach proposed to use PL DDR for decoding and PS DDR for encoding so that DDR bandwidth would be enough to support high bandwidth VCU applications requiring simultaneous encoder and decoder operations and transcoding at 4k@60fps. This approach makes the most effective use of limited AXI4 read/write issuance capability in minimizing latency for the decoder. DMA buffer sharing requirements determine how capture, display, and intermediate processing stages should be mapped to the PS or PL DDR.
This module enables capture of video from an HDMI Rx Subsystem implemented in the PL. The video can be displayed through HDMI Tx through the PL and recorded in SD cards or USB/SATA drives. The module can Stream-in or Stream-out encoded data through an Ethernet interface. This module supports NV12, NV16, XV15, and XV20 pixel formats.
This design supports the following video interfaces:
Sources:
- HDMI-Rx capture pipeline implemented in the PL.
- File source (SD card, USB storage, SATA hard disk).
- Stream-In from network or internet.
Sinks:
- HDMI-Tx display pipeline implemented in the PL.
VCU Codec:
- Video Encode/Decode capability using VCU hard block in PL
- AVC/HEVC encoding
- Encoder/decoder parameter configuration.
Video format:
- NV12
- NV16
- XV15
- XV20
Supported Resolution:
The table below provides the supported resolution from command line app only in this design.
| Resolution | Command Line | |
| Single Stream | Multi-stream | |
| 4kp60 | √ | NA |
| 4kp30 | √ | NA |
| 1080p60 | √ | NA |
√ - Supported
NA – Not applicable
x – Not supported
The below table gives information about the features supported in this design.
| Pipeline | Input source | Format | Output Type | Resolution | VCU codec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Capture--> Display(Pass-through pipeline) | HDMI-Rx | NV12, NV16, XV15, XV20 | HDMI-Tx | 4KP/1080p | None |
Capture--> Encode--> Decode--> Display | HDMI-Rx | NV12, NV16, XV15, XV20 | HDMI-Tx | 4KP/1080p | HEVC/AVC |
Record/Stream-Out pipeline | HDMI-Rx | NV12, NV16, XV15, XV20 | File Sink/ Stream-Out | 4K/1080p | HEVC/AVC |
File/Streaming Playback pipeline | File Source/ Stream-In | NV12, NV16, XV15, XV20 | HDMI-Tx | 4K/1080p | HEVC/AVC |
The below figure shows the PL DDR HDMI design hardware block diagram.
The below figure shows the PL DDR HDMI design software block diagram.
1.1 Board Setup
Refer below link for Board Setup
1.2 Run Flow
The TRD package is released with the source code, Vivado project, Petalinux BSP, and SD card image that enables the user to run the demonstration. It also includes the binaries necessary to configure and boot the ZCU106 board. Prior to running the steps mentioned in this wiki page, download the TRD package and extract its contents to a directory referred to as ‘TRD_HOME' which is the home directory.
Refer below link to download all TRD contents.
TRD package contents are placed in the following directory structure. The user needs to copy all the files from the $TRD_HOME/images/vcu_plddr_hdmi/ to FAT32 formatted SD card directory.
└── rdf0428-zcu106-vcu-trd-2019-1
├── apu
│ ├── apps
│ ├── vcu_petalinux_bsp
│ ├── vcu_sdx
│ └── ws_bypass
├── host_x86
│ └── host_package
├── images
│ ├── vcu_10g
│ ├── vcu_audio
│ ├── vcu_hdmirx
│ ├── vcu_hdmitx
│ ├── vcu_pcie
│ ├── vcu_plddr_hdmi
│ ├── vcu_sdirx
│ ├── vcu_sdirxtx
│ ├── vcu_sditx
│ ├── vcu_sdx
│ └── vcu_trd
├── pl
│ ├── constrs
│ ├── pre-built
│ ├── scripts
│ └── srcs
└── README.txt
TRD package contents specific to VCU PL DDR HDMI design are placed in the following directory structure.
└── rdf0428-zcu106-vcu-trd-2019-1
├── apu
│ ├── apps
│ ├── vcu_petalinux_bsp
│ ├── vcu_sdx
│ └── ws_bypass
├── host_x86
│ └── host_package
├── images
│ ├── vcu_plddr_hdmi
│ │ ├── autostart.sh
│ │ ├── bin
│ │ ├── BOOT.BIN
│ │ ├── config
│ │ ├── image.ub
│ │ ├── system.dtb
│ │ └── vcu
├── pl
│ ├── constrs
│ ├── pre-built
│ │ ├── vcu_plddr_hdmi
│ ├── scripts
│ │ └── vcu_plddr_hdmi_proj.tcl
│ │ └── vcu_plddr_hdmi_bd.tcl
│ └── srcs
└── README.txt
configuration files(input.cfg) for various resolutions are placed in the following directory structure in /media/card.
config/ ├── 1080p60 │ ├── Display │ ├── Record │ ├── Stream-in │ └── Stream-out ├── 4kp30 │ ├── Display │ ├── Record │ ├── Stream-in │ └── Stream-out ├── 4kp60 │ ├── Display │ ├── Record │ ├── Stream-in │ └── Stream-out └── input.cfg
1.2.1 GStreamer Application (vcu_gst_app)
The vcu_gst_app is a command line multi-threaded linux application. The command line application requires an input configuration file (input.cfg) to be provided in the plain text.
Before execution of vcu_gst_app, run below modetest command manually in the background to set CRTC configurations in case of PL DDR HDMI design.
% modetest -D a0070000.v_mix -s 37:3840x2160-60@BG24 &
Execution of the application is shown below:
% vcu_gst_app < path to *.cfg file>
Example:
4kp60 XV20 HEVC_HIGH Display Pipeline execution
% vcu_gst_app /media/card/config/4kp60/Display/Single_4kp60_HEVC_HIGH.cfg
4kp60 XV20 HEVC_HIGH Record Pipeline execution
% vcu_gst_app /media/card/config/4kp60/Record/Single_4kp60_HEVC_HIGH.cfg
4kp60 XV20 HEVC_HIGH Stream-out Pipeline execution
% vcu_gst_app /media/card/config/4kp60/Stream-out/Single_4kp60_HEVC_HIGH.cfg
4kp60 XV20 HEVC_HIGH Stream-in Pipeline execution
% vcu_gst_app /media/card/config/4kp60/Stream-in/input.cfg
NOTE: Make sure HDMI-Rx should be configured to 4kp60 mode.
To measure the latency of the pipeline, run the below command. The latency data is huge, so dump it to a file.
% GST_DEBUG="GST_TRACER:7" GST_TRACERS="latency;scheduletime" ./vcu_gst_app ./input.cfg >& dump_log.txt
Refer below link for detailed run flow steps
1.3 Build Flow
Refer below link for detailed build flow steps
2 Other Information
2.1 Known Issues
Frame drop is observed with AVC 4kp60 use-cases.
- Frequency: Random
- Workaround: Please refer AR# 72324: 2019.1 - Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC VCU to resolve frame drop issue with AVC 4kp60 use-cases.
- Frequency: Random
Block noise is observed with AVC 4k use-cases.
- Frequency: Random
- Workaround: None
- Frequency: Random
- Hardware Design timing is failed around -0.040 to -0.050 in WNS
- For VCU related known issues please refer AR# 72293: PetaLinux 2019.1 - Product Update Release Notes and Known Issues.
2.2 Limitations
- For VCU related limitations please refer AR# 72293: PetaLinux 2019.1 - Product Update Release Notes and Known Issues and PG252 link.
2.3 Optimum VCU Encoder parameters for use-cases
Video streaming:
- Video streaming use-case requires very stable bitrate graph for all pictures.
- It is good to avoid periodic large Intra pictures during the encoding session
- Low-latency rate control (hardware RC) is the preferred control-rate for video streaming, it tries to maintain equal amount frame sizes for all pictures.
- Good to avoid periodic Intra frames instead use low-delay-p (IPPPPP…)
- VBR is not a preferred mode of streaming.
Performance: AVC Encoder settings:
- It is preferred to use 8 or higher slices for better AVC encoder performance.
- AVC standard does not support Tile mode processing which results in the processing of MB rows sequentially for entropy coding.
Quality: Low bitrate AVC encoding:
- Enable profile=high and use qp-mode=auto for low-bitrate encoding use-cases.
- The high profile enables 8x8 transform which results in better video quality at low bitrates.
3 Appendix A - Input Configuration File (input.cfg)
The example configuration files are stored at /media/card/config/ folder.
Common Configuration:
It is the starting point of common configuration.
Num of Input:
Provide the number of input. this is always 1 for this design.
Output:
Select the video interface.
Options: HDMI
Out Type:
Options: display, record, and stream
Display Rate:
Pipeline frame rate.
Options: 30 FPS or 60 FPS for each stream.
Exit:
It indicates to the application that the configuration is over.
Input Configuration:
It is the starting point of the input configuration.
Input Num:
Starting Nth input configuration.
Options: 1
Input Type:
Input source type.
Options: HDMI, File, Stream
Uri:
File path or Network URL. Applicable for file playback and stream-in pipeline only. Supported file formats for playback are ts, mp4, and mkv.
Options: file:///media/usb/abc.ts (for file path), udp://192.168.25.89:5004/ (for Network streaming, Here 192.168.25.89 is IP address and 5004 is port no)
Raw:
To tell the pipeline is processed or pass-through.
Options: True, False
Width:
The width of the live source.
Options: 3840, 1920
Height:
The height of the live source.
Options: 2160, 1080
Format:
The format of input data.
Options: NV12, NV16, XV15, XV20
Exit:
It indicates to the application that the configuration is over.
Encoder Configuration:
It is the starting point of encoder configuration.
Encoder Num:
Starting Nth encoder configuration.
Options: 1
Encoder Name:
Name of the encoder.
Options: AVC, HEVC
Profile:
Name of the profile.
Options: For NV12: baseline, main or high for AVC and main for HEVC.
For NV16, XV15, XV20: high for AVC and main for HEVC.
Rate Control:
Rate control options.
Options: CBR, VBR, and low-latency.
Filler Data:
Filler Data NAL units for CBR rate control.
Options: True, False
QP:
QP control mode used by the VCU encoder.
Options: Uniform, Auto
L2 Cache:
Enable or Disable L2Cache buffer in encoding process.
Options: True, False
Latency Mode:
Encoder latency mode.
Options: normal, sub_frame
Low Bandwidth:
If enabled, decrease the vertical search range used for P-frame motion estimation to reduce the bandwidth.
Options: True, False
Gop Mode:
Group of Pictures mode.
Options: Basic, low_delay_p, low_delay_b
Bitrate:
Target bitrate in Kbps
Options: 1-60000
B Frames:
Number of B-frames between two consecutive P-frames
Options: 0-4
Slice:
The number of slices produced for each frame. Each slice contains one or more complete macroblock/CTU row(s). Slices are distributed over the frame as regularly as possible. If slice-size is defined as well more slices may be produced to fit the slice-size requirement.
Options:
4-22 4kp resolution with HEVC codec
4-32 4kp resolution with AVC codec
4-32 1080p resolution with HEVC codec
4-32 1080p resolution with AVC codec
GoP Length:
The distance between two consecutive I frames
Options: 1-1000
Preset:
Options: HEVC_HIGH, HEVC_MEDIUM, HEVC_LOW, AVC_HIGH, AVC_MEDIUM, AVC_LOW, Custom
Exit
It indicates to the application that the configuration is over.
Record Configuration:
It is the starting point of record configuration.
Record Num:
Starting Nth record configuration.
Options: 1
Out-File Name:
Record file path.
Options: /media/usb/abc.ts
Duration:
Duration in minutes.
Options: 1-3
Exit
It indicates to the application that the configuration is over.
Streaming Configuration:
It is the starting point of streaming configuration.
Streaming Num:
Starting Nth Streaming configuration.
Options: 1
Host IP:
The host to send the packets to
Options: 192.168.25.89 or Windows PC IP
Port:
The port to send the packets to
Options: 5004, 5008, 5012 and 5016
Exit
It indicates to the application that the configuration is over.
Trace Configuration:
It is the starting point of trace configuration.
FPS Info:
To display fps info on the console.
Options: True, False
APM Info:
To display APM counter number on the console.
Options: True, False
Pipeline Info:
To display pipeline info on console.
Options: True, False
Exit
It indicates to the application that the configuration is over.
4 Appendix B
- To check the link status, resolution and video node of the HDMI input source, run below xmedia-ctl command where "media0" indicates media node for the HDMI input source.
$ xmedia-ctl -p -d /dev/media0
When HDMI source is connected to 4KP60 resolution, it shows:
root@zcu106_vcu_trd:~# xmedia-ctl -p -d /dev/media0
Media controller API version 4.19.0
Media device information
------------------------
driver xilinx-video
model Xilinx Video Composite Device
serial
bus info
hw revision 0x0
driver version 4.19.0
Device topology
- entity 1: vcap_hdmi output 0 (1 pad, 1 link)
type Node subtype V4L flags 0
device node name /dev/video0 -----> Video node for HDMI Rx source
pad0: Sink
<- "a0080000.v_proc_ss":1 [ENABLED]
- entity 5: a0080000.v_proc_ss (2 pads, 2 links)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev0
pad0: Sink
[fmt:VYYUYY10_4X20/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb]
<- "a0000000.v_hdmi_rx_ss":0 [ENABLED]
pad1: Source
[fmt:VYYUYY10_4X20/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:srgb]
-> "vcap_hdmi output 0":0 [ENABLED]
- entity 8: a0000000.v_hdmi_rx_ss (1 pad, 1 link)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev1
pad0: Source
[fmt:RBG888_1X24/3840x2160 field:none colorspace:srgb]
[dv.caps:BT.656/1120 min:0x0@25000000 max:4096x2160@297000000 stds:CEA-861,DMT,CVT,GTF caps:progressive,reduced-blanking,custom
]
[dv.detect:BT.656/1120 3840x2160p60 (4400x2250) stds:CEA-861 flags:CE-video] -----> Resolution and Frame-rate of HDMI Rx source
-> "a0080000.v_proc_ss":0 [ENABLED]
NOTE: Check resolution and frame-rate of "dv.detect" under "v_hdmi_rx_ss" node.
When the HDMI source is not connected, it shows:
root@zcu106_vcu_trd:~# xmedia-ctl -p -d /dev/media0
Media controller API version 4.19.0
Media device information
------------------------
driver xilinx-video
model Xilinx Video Composite Device
serial
bus info
hw revision 0x0
driver version 4.19.0
Device topology
- entity 1: vcap_hdmi output 0 (1 pad, 1 link)
type Node subtype V4L flags 0
device node name /dev/video0 -----> Video node for HDMI Rx source
pad0: Sink
<- "a0080000.v_proc_ss":1 [ENABLED]
- entity 5: a0080000.v_proc_ss (2 pads, 2 links)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev0
pad0: Sink
[fmt:VYYUYY10_4X20/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb]
<- "a0000000.v_hdmi_rx_ss":0 [ENABLED]
pad1: Source
[fmt:VYYUYY10_4X20/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:srgb]
-> "vcap_hdmi output 0":0 [ENABLED]
- entity 8: a0000000.v_hdmi_rx_ss (1 pad, 1 link)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev1
pad0: Source
[fmt:RBG888_1X24/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb]
[dv.caps:BT.656/1120 min:0x0@25000000 max:4096x2160@297000000 stds:CEA-861,DMT,CVT,GTF caps:progressive,reduced-blanking,custom
]
[dv.query:no-link] -----> HDMI Rx Link Status
-> "a0080000.v_proc_ss":0 [ENABLED]
NOTE: Here "dv.query:no-link" under "v_hdmi_rx_ss" node shows HDMI-Rx source is not connected or HDMI-Rx source is not active(Try waking up the device by pressing a key on remote).
- Follow the below steps to switch the HDMI-Rx resolution from 1080p60 to 4kp60.
- Check current HDMI Input Source Resolution (1080p60) by following the above-mentioned steps.
- Run vcu_gst_app for current HDMI resolution (1080p60) by executing the following command.
$ vcu_gst_app /media/card/config/input.cfg
Below configurations needs to be set in input.cfg for HDMI-1080p60.
Common Configuration : START Num Of Input : 1 Output : HDMI Out Type : Display Frame Rate : 60 Exit Input Configuration : START Input Num : 1 Input Type : hdmi Raw : TRUE Width : 1920 Height : 1080 Format : XV20 Exit
- Change Resolution of HDMI Input Source from 1080p60 to 4kp60 by following below steps.
- Set the HDMI source resolution to 4kp60 (Homepage → Settings → Display & Sound → Resolution → change to 4kp60).
- Save the configuration to take place the change.
- Verify the desired HDMI Input Source Resolution (4kp60) by following the above-mentioned steps.
- Change Resolution of HDMI Input Source from 1080p60 to 4kp60 by following below steps.
- If HDMI Tx link-up issue is observed after Linux booting, use the following command to get the blue screen on HDMI-Tx.
% modetest -D a0070000.v_mix -s 37:3840x2160-60@BG24 &
- The table below list the parameters that differ with respect to pixel format.
| Pixel Format | GStreamer Format | Media Bus Format | GStreamer HEVC Profile | GStreamer AVC Profile | Kmssink Plane-id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XV20 | NV16_10LE32 | UYVY10_1X20 | main-422-10 | high-4:2:2 | 30 |
| XV15 | NV12_10LE32 | VYYUYY10_4X20 | main-10 | high-10 | 31 |
| NV16 | NV16 | UYVY8_1X16 | main-422 | high-4:2:2 | 32 |
| NV12 | NV12 | VYYUYY8_1X24 | main | high | 33 |
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to display XV20 video on HDMI-Tx using pass-through GStreamer pipeline. Where "video0" indicates a video node for the input source.
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 io-mode=4 ! video/x-raw, width=3840, height=2160, format=NV16_10LE32, framerate=60/1 ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! fpsdisplaysink text-overlay=false video-sink="kmssink bus-id="a0070000.v_mix" plane-id=30"
NOTE: Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format.
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to display XV20 video on HDMI-Tx using processed GStreamer pipeline (capture → encode → decode → display). Where "video0" indicates a video node for the input source.
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 io-mode=4 ! video/x-raw, width=3840, height=2160, format=NV16_10LE32, framerate=60/1 ! omxh265enc qp-mode=auto gop-mode=basic gop-length=60 b-frames=0 target-bitrate=60000 num-slices=8 control-rate=constant prefetch-buffer=true low-bandwidth=false filler-data=true cpb-size=1000 initial-delay=500 ! video/x-h265, profile=main-422-10, alignment=au ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! omxh265dec internal-entropy-buffers=5 low-latency=0 ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! fpsdisplaysink text-overlay=false video-sink="kmssink bus-id="a0070000.v_mix" plane-id=30"
NOTE: Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format.
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to record XV20 video using GStreamer pipeline. Where "video0" indicates a video node for the input source.
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 io-mode=4 num-buffers=3600 ! video/x-raw, width=3840, height=2160, format=NV16_10LE32, framerate=60/1 ! omxh265enc qp-mode=auto gop-mode=basic gop-length=60 b-frames=0 target-bitrate=60000 num-slices=8 control-rate=constant prefetch-buffer=true low-bandwidth=false filler-data=true cpb-size=1000 initial-delay=500 ! video/x-h265, profile=main-422-10, alignment=au ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! mpegtsmux alignment=7 name=mux ! filesink location="/run/test.ts"
NOTE: File location should be USB-3.0/SATA/RAMFS to avoid the read-write bandwidth issue. Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format.
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to play XV20 recorded file on HDMI-Tx using the GStreamer pipeline.
$ gst-launch-1.0 uridecodebin uri="file:///run/test.ts" ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! fpsdisplaysink text-overlay=false video-sink="kmssink bus-id="a0070000.v_mix" plane-id=30"
NOTE: File location should be USB-3.0/SATA/RAMFS to avoid the read-write bandwidth issue. Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format.
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to stream-out XV20 video using GStreamer pipeline. Where "video0" indicates a video node for the input source.
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 io-mode=4 ! video/x-raw, width=3840, height=2160, format=NV16_10LE32, framerate=60/1 ! omxh265enc qp-mode=auto gop-mode=basic gop-length=60 b-frames=0 target-bitrate=60000 num-slices=8 control-rate=constant prefetch-buffer=true low-bandwidth=false filler-data=true cpb-size=1000 initial-delay=500 periodicity-idr=60 ! video/x-h265, profile=main-422-10, alignment=au ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! mpegtsmux alignment=7 name=mux ! rtpmp2tpay ! udpsink host=192.168.25.89 port=5004
NOTE: Here 192.168.25.89 is host/client IP address and 5004 is port no. Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format.
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to display XV20 stream-in video on HDMI-Tx using GStreamer pipeline where 5004 is port no.
$ gst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 buffer-size=60000000 caps="application/x-rtp, clock-rate=90000" ! rtpjitterbuffer latency=1000 ! rtpmp2tdepay ! tsparse ! video/mpegts ! tsdemux name=demux ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! h265parse ! video/x-h265, profile=main-422-10, alignment=au ! omxh265dec internal-entropy-buffers=5 low-latency=0 ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! fpsdisplaysink text-overlay=false video-sink="kmssink bus-id="a0070000.v_mix" plane-id=30"
NOTE: Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format.
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to stream-out XV20 video using low-latency GStreamer pipeline. Where "video0" indicates a video node for the input source.
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 io-mode=4 ! video/x-raw, width=3840, height=2160, format=NV16_10LE32, framerate=60/1 ! omxh265enc qp-mode=auto gop-mode=basic gop-length=60 b-frames=0 target-bitrate=60000 num-slices=8 control-rate=low-latency prefetch-buffer=true low-bandwidth=false filler-data=true cpb-size=1000 initial-delay=500 periodicity-idr=60 ! video/x-h265, profile=main-422-10, alignment=nal ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! mpegtsmux alignment=7 name=mux ! rtpmp2tpay ! udpsink host=192.168.25.89 port=5004
NOTE: Here 192.168.25.89 is host/client IP address and 5004 is port no. Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format.
- Run the following gst-launch-1.0 command to display XV20 stream-in video on HDMI-Tx using low-latency GStreamer pipeline where 5004 is port no.
$ gst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 buffer-size=60000000 caps="application/x-rtp, clock-rate=90000" ! rtpjitterbuffer latency=1000 ! rtpmp2tdepay ! tsparse ! video/mpegts ! tsdemux name=demux ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! h265parse ! video/x-h265, profile=main-422-10, alignment=nal ! omxh265dec internal-entropy-buffers=5 low-latency=1 ! queue max-size-bytes=0 ! fpsdisplaysink text-overlay=false video-sink="kmssink bus-id="a0070000.v_mix" plane-id=30"
NOTE: Refer above table to run the same pipeline for a different format. Low latency stream-in pipeline is not supported in vcu_gst_app.
Notes for gst-launch-1.0 commands:
- Video node for HDMI Rx source can be checked using xmedia-ctl command. Run below xmedia-ctl command to check video node for HDMI Rx source where "media0" indicates media node for HDMI input source.
$ xmedia-ctl -p -d /dev/media0
- Make sure HDMI-Rx media pipeline is configured for 4kp60 resolution and source/sink have the same colour format for connected nodes. For XV20 format, run below xmedia-ctl commands to set resolution and format of HDMI scaler node where "media0" indicates media node for HDMI input source.
When HDMI Input Source is NVIDIA SHIELD
$ xmedia-ctl -d /dev/media0 -V "\"a0080000.v_proc_ss\":0 [fmt:RBG888_1X24/3840x2160 field:none]" $ xmedia-ctl -d /dev/media0 -V "\"a0080000.v_proc_ss\":1 [fmt:UYVY10_1X20/3840x2160 field:none]"
NOTE: Make sure NVIDIA SHIELD is configured for 4kp resolution and RBG888_1X24 format. Refer above table to run the same commands for a different format.
When HDMI Input Source is ABOX
$ xmedia-ctl -d /dev/media0 -V "\"a0080000.v_proc_ss\":0 [fmt:VYYUYY8_1X24/3840x2160 field:none]" $ xmedia-ctl -d /dev/media0 -V "\"a0080000.v_proc_ss\":1 [fmt:UYVY10_1X20/3840x2160 field:none]"
NOTE: Make sure ABOX is configured for 4kp resolution and VYYUYY8_1X24 format. Refer above table to run the same commands for a different format.
© Copyright 2019 - 2022 Xilinx Inc. Privacy Policy