This page demonstrates the usage of remoteproc kernel driver by the master processor (A72) on the VCK190 to load remote application firmware on the R5 processor. The example below has been tested on tool version used for this example is 2020.2 and 2021.1
Table of Contents
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
Launch Vitis IDE.
File → New Application Project
Create a new platform from hardware (XSA). Select from the included xsa’s or click on browse and import your xsa to create the platform project.
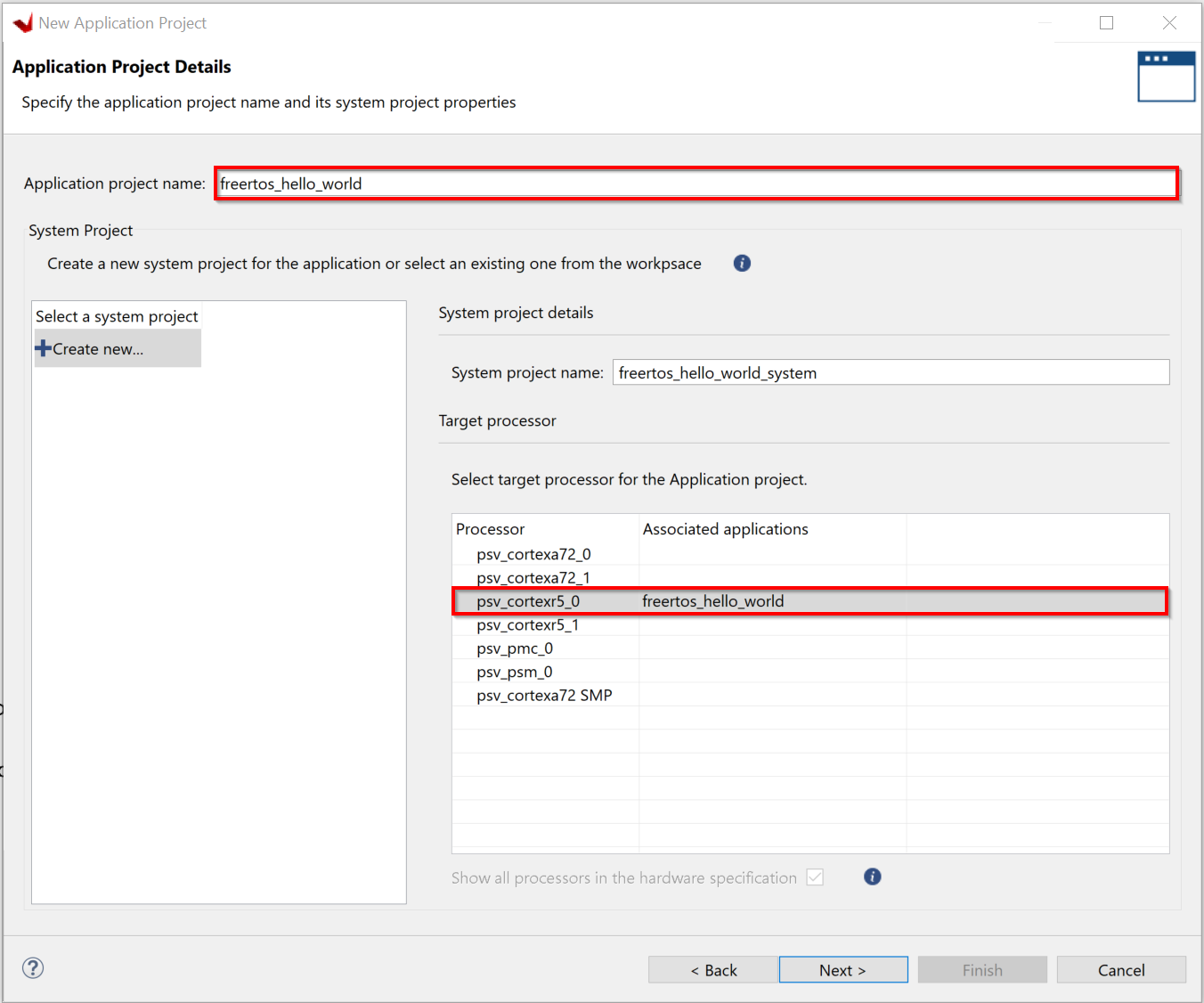
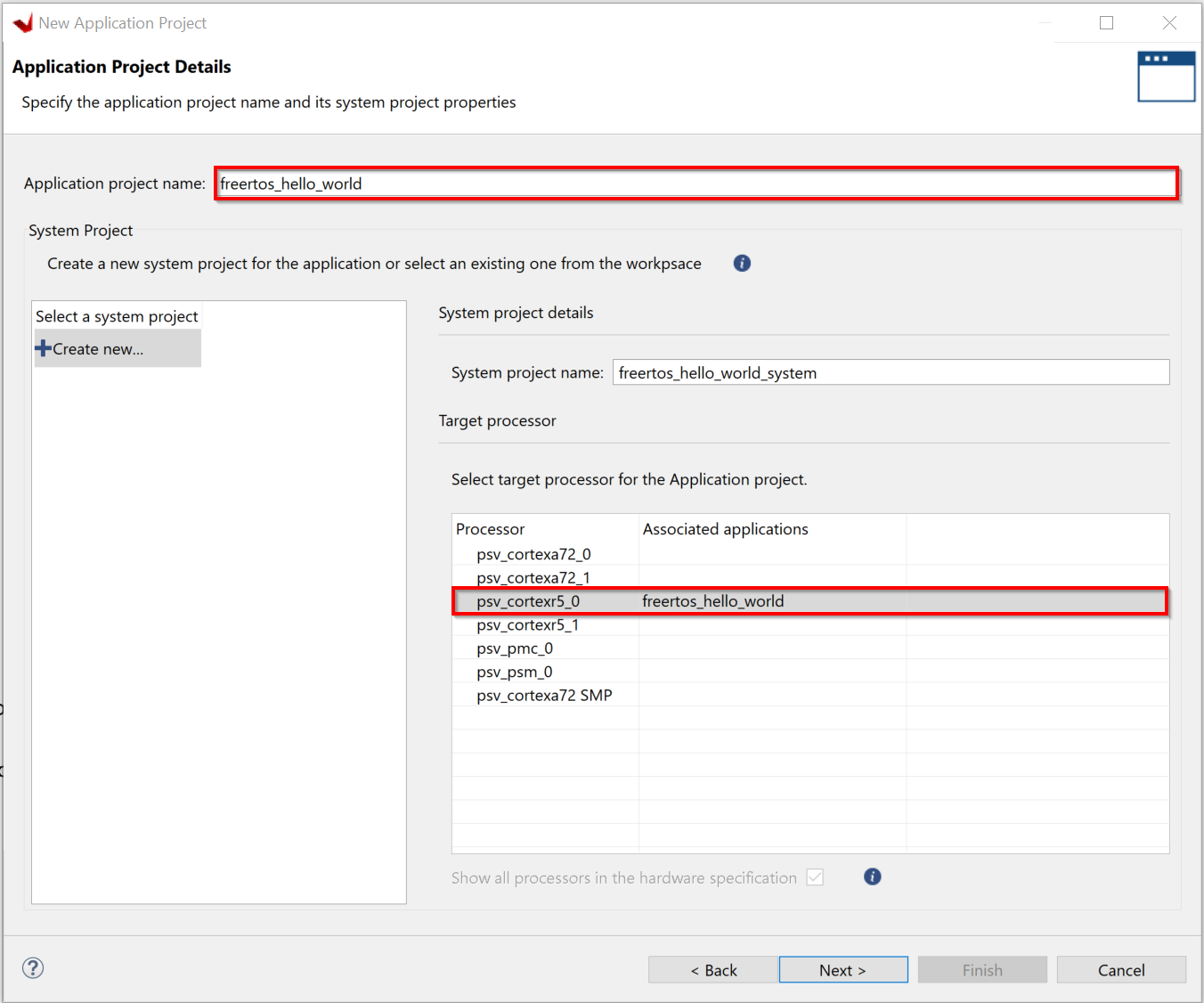
Specify the application project name; freertos_hello_world_r50 and select psv_cortexr5_0 as the target processor from the list of processors.
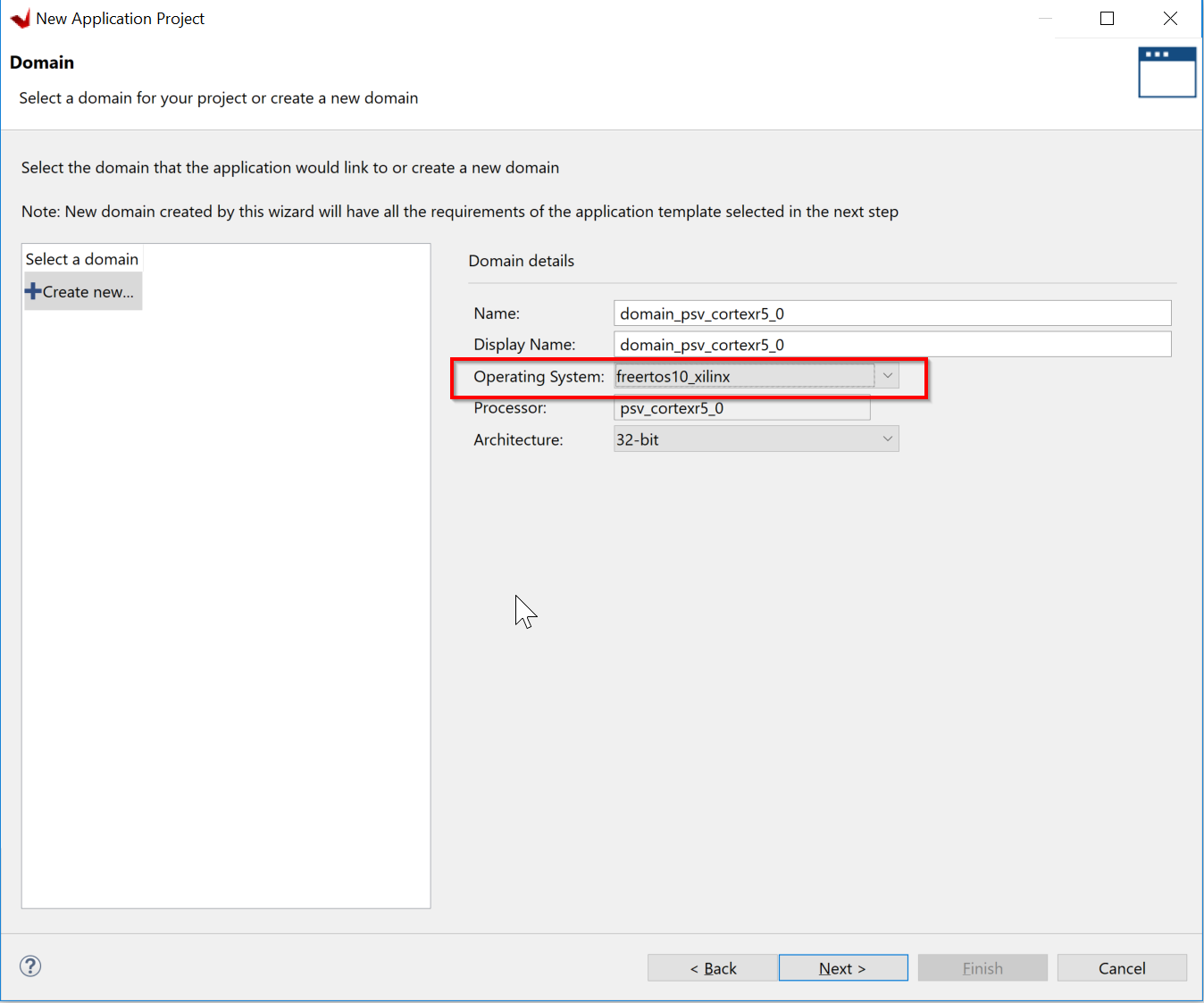
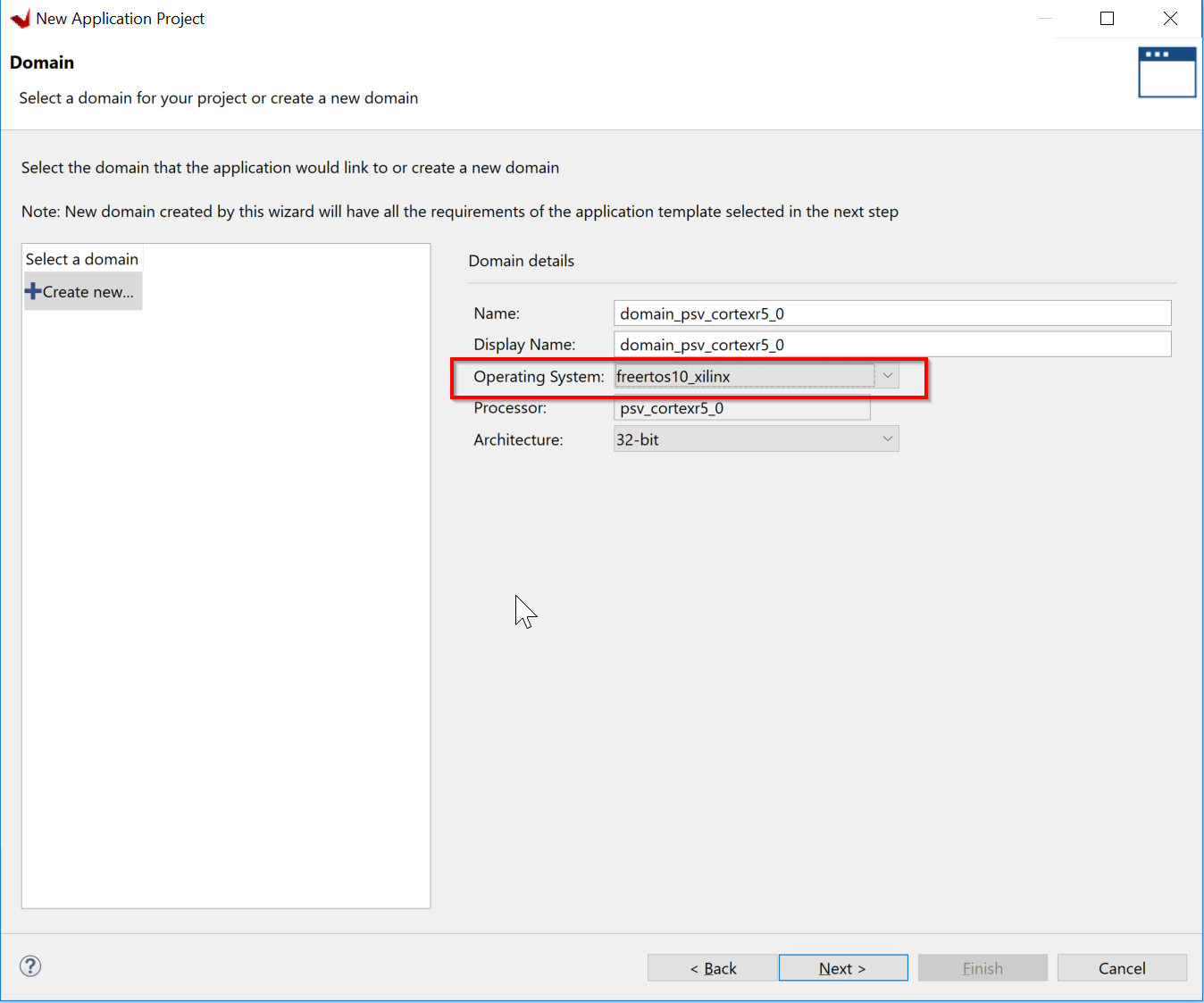
Create a new domain for your project. Select freertos10_xilinx as the Operating System from the drop down list.
Select the FreeRTOS hello world template and hit Finish.
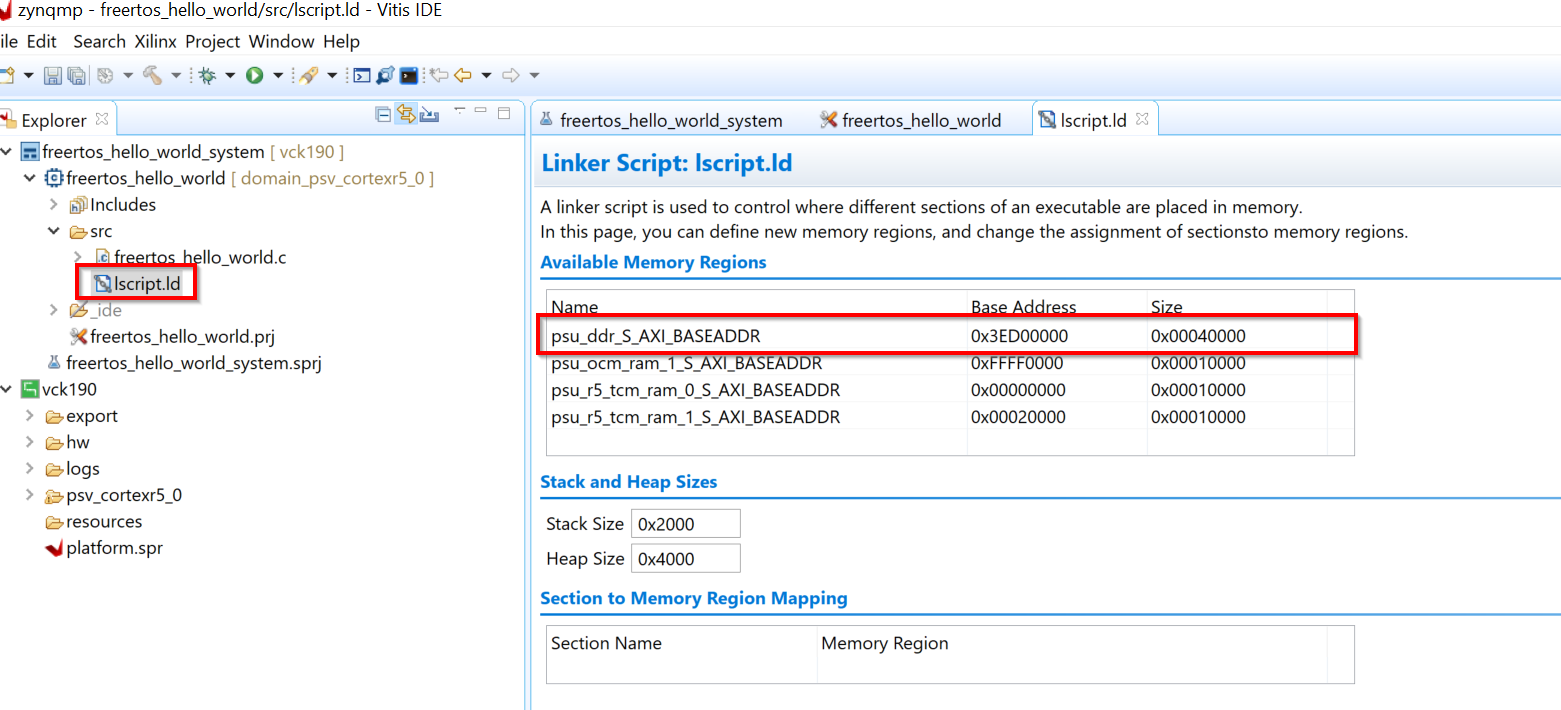
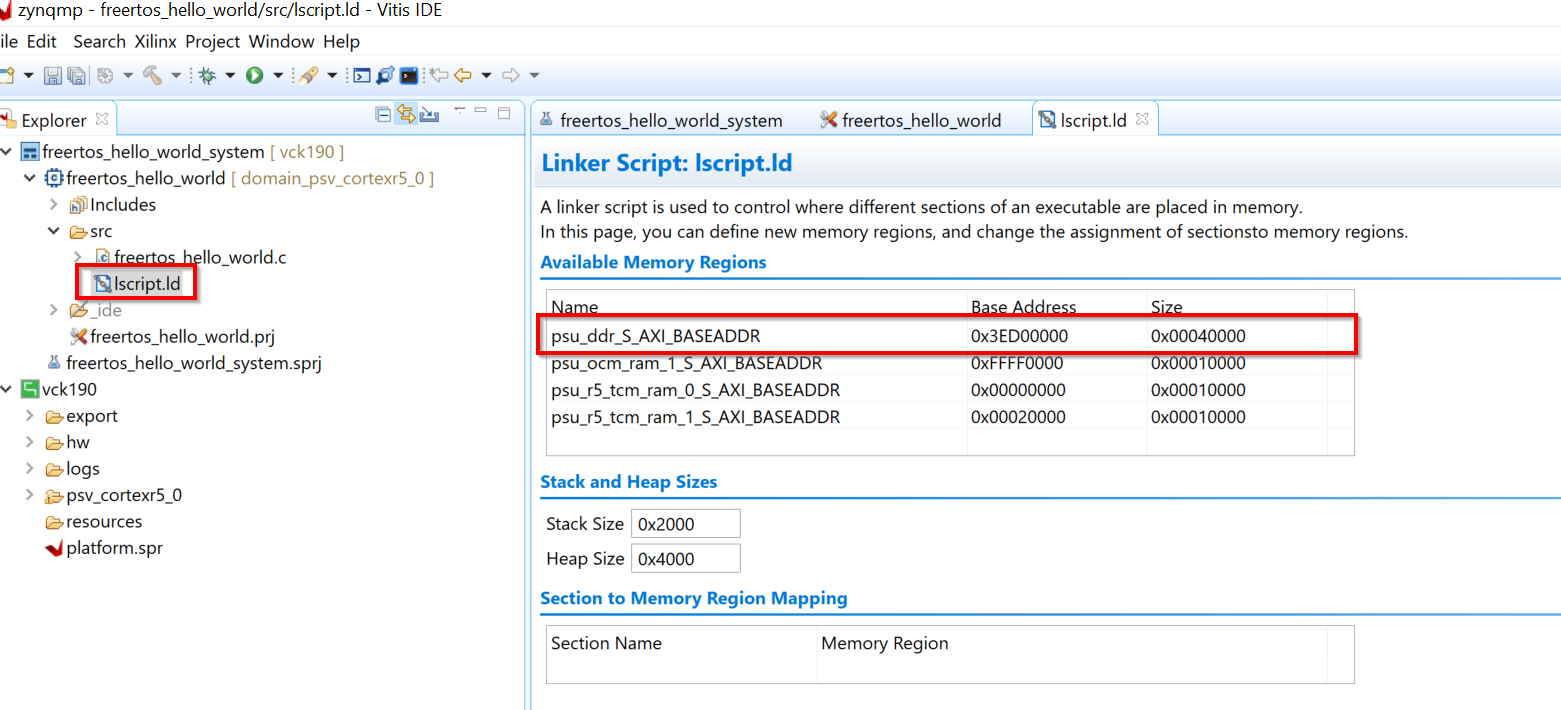
Modify the lscript.ld so that the RPU application elf is running out of DDR. This section will also be carved out and reserved for the RPU firmware in the Linux device-tree so that it does not get used by Linux.
Build the application project. The generated elf file in the Debug/Release folder of the application project will be installed in the rootfs of the PetaLinux project.
Build the PetaLinux project
...
Create a PetaLinux application
Code Block $ petalinux-create -t apps --template install -n freertos-hello-world-r50 --enable
Replace the default application installed by the template with the freertos_hello_world elf built in Xilinx Vitis for the R5-0 processor into the project-spec/meta-user/recipes-apps/freertos-hello-world-r50/files/ folder.
Code Block cp <vitis-app-proj>/Debug/freertos_hello_world_r50.elf <plnx-proj-root>/project-spec/meta-user/recipes-apps/freertos-hello-world-r50/files/
Modify the recipe for the application to include the RPU firmware ELF built in Vitis into the the rootfs.
Code Block $ vim project-spec/meta-user/recipes-apps/freertos-hello-world-r50/freertos-hello-world-r50.bb # # This file is the freertos-hello-world-r50 recipe. # SUMMARY = "Simple freertos-hello-world-r50 application" SECTION = "PETALINUX/apps" LICENSE = "MIT" LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = "file://${COMMON_LICENSE_DIR}/MIT;md5=0835ade698e0bcf8506ecda2f7b4f302" SRC_URI = "file://freertos_hello_world_r50.elf" S = "${WORKDIR}" INSANE_SKIP_${PN} = "arch" do_install() { install -d ${D}/lib/firmware install -m 0644 ${S}/freertos_hello_world_r50.elf ${D}/lib/firmware/freertos_hello_world_r50.elf } FILES_${PN} = "/lib/firmware/freertos_hello_world_r50.elf"Copy the contents of the openamp.dtsi from <plnx-proj>/project-spec/meta-user/recipes-bsp/device-tree/files into the system-user.dtsi. Please see the dtsi below for reference. NOTE: the node entry for rproc_0_reserved has the same memory region as the one carved out in the lscript.ld in the Vitis application.
system-user.dtsi for 2020.2
Code Block /include/ "system-conf.dtsi" / { }; / { reserved-memory { #address-cells = <2>; #size-cells = <2>; ranges; rpu0vdev0vring0: rpu0vdev0vring0@3ed40000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed40000 0x0 0x4000>; }; rpu0vdev0vring1: rpu0vdev0vring1@3ed44000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed44000 0x0 0x4000>; }; rpu0vdev0buffer: rpu0vdev0buffer@3ed48000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed48000 0x0 0x100000>; }; rproc_0_reserved: rproc@3ed00000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed00000 0x0 0x40000>; }; }; zynqmp-rpu { compatible = "xlnx,zynqmp-r5-remoteproc-1.0"; #address-cells = <2>; #size-cells = <2>; ranges; core_conf = "split"; reg = <0x0 0xFF9A0000 0x0 0x10000>; r5_0: r5@0 { #address-cells = <2>; #size-cells = <2>; ranges; memory-region = <&rproc_0_reserved>, <&rpu0vdev0buffer>, <&rpu0vdev0vring0>, <&rpu0vdev0vring1>; pnode-id = <0x18110005>; mboxes = <&ipi_mailbox_rpu0 0>, <&ipi_mailbox_rpu0 1>; mbox-names = "tx", "rx"; tcm_0_a: tcm_0@0 { reg = <0x0 0xFFE00000 0x0 0x10000>; pnode-id = <0x1831800b>; }; tcm_0_b: tcm_0@1 { reg = <0x0 0xFFE20000 0x0 0x10000>; pnode-id = <0x1831800c>; }; }; }; zynqmp_ipi1 { compatible = "xlnx,zynqmp-ipi-mailbox"; interrupt-parent = <&gic>; interrupts = <0 33 4>; xlnx,ipi-id = <5>; #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <1>; ranges; /* APU<->RPU0 IPI mailbox controller */ ipi_mailbox_rpu0: mailbox@ff990600 { reg = <0xff3f0ac0 0x20>, <0xff3f0ae0 0x20>, <0xff3f0740 0x20>, <0xff3f0760 0x20>; reg-names = "local_request_region", "local_response_region", "remote_request_region", "remote_response_region"; #mbox-cells = <1>; xlnx,ipi-id = <3>; }; }; };
system-user.dtsi for 2021.1
Code Block
$ petalinux-build $ petalinux-package --boot --plm --psmfw --u-boot --dtb
Running the firmware
The steps below show how to boot the images using SD boot mode.
From your <plnx-proj-root>/images/linux folder, copy the BOOT.bin, image.ub and boot.scr to the SD card.
| Note |
|---|
Known issue: In 2020.x, the TTC is put in reset by the PM framework. As a workaround, you will need to request for the TTC node (PM_DEV_TTC_0 (0x18224024U)) using the SysFS interface. |
| Code Block |
|---|
echo pm_request_node 0x18224024 0x7 0x64 0 > /sys/kernel/debug/zynqmp-firmware/pm |
The list of device nodes and their respective values can be found in the Versal Software Developers Guide UG1304 here https://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/sw_manuals/xilinx2020_1/ug1304-versal-acap-ssdg.pdf#page=217
Load and start the firmware using remoteproc sysfs.
| Code Block |
|---|
echo freertos_hello_world_r50.elf > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/firmware
echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state |
Below is a snippet of the boot console.
...
/include/ "system-conf.dtsi" / { reserved-memory { #address-cells = <2>; #size-cells = <2>; ranges; rproc_0_reserved: rproc@3ed00000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed00000 0x0 0x40000>; }; rpu0vdev0vring0: rpu0vdev0vring0@3ed40000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed40000 0x0 0x4000>; }; rpu0vdev0vring1: rpu0vdev0vring1@3ed44000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed44000 0x0 0x4000>; }; rpu0vdev0buffer: rpu0vdev0buffer@3ed48000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ed48000 0x0 0x100000>; }; rproc_1_reserved: rproc@3ef00000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ef00000 0x0 0x40000>; }; rpu1vdev0vring0: rpu1vdev0vring0@3ef40000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ef40000 0x0 0x4000>; }; rpu1vdev0vring1: rpu1vdev0vring1@3ef44000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0x3ef44000 0x0 0x4000>; }; rpu1vdev0buffer: rpu1vdev0buffer@3ef48000 { no-map; compatible = "shared-dma-pool"; reg = <0x0 0x3ef48000 0x0 0x100000>; }; }; tcm_0a@ffe00000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0xffe00000 0x0 0x10000>; phandle = <0x40>; status = "okay"; compatible = "mmio-sram"; }; tcm_0b@ffe20000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0xffe20000 0x0 0x10000>; phandle = <0x41>; status = "okay"; compatible = "mmio-sram"; }; tcm_0a@ffe90000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0xffe90000 0x0 0x10000>; phandle = <0x42>; status = "okay"; compatible = "mmio-sram"; }; tcm_0b@ffeb0000 { no-map; reg = <0x0 0xffeb0000 0x0 0x10000>; phandle = <0x43>; status = "okay"; compatible = "mmio-sram"; }; rf5ss@ff9a0000 { compatible = "xlnx,zynqmp-r5-remoteproc"; #address-cells = <0x2>; #size-cells = <0x2>; ranges; xlnx,cluster-mode = <1>; reg = <0x0 0xff9a0000 0x0 0x10000>; r5f_0 { compatible = "xilinx,r5f"; #address-cells = <0x2>; #size-cells = <0x2>; ranges; sram = <0x40 0x41>; memory-region = <&rproc_0_reserved>, <&rpu0vdev0buffer>, <&rpu0vdev0vring0>, <&rpu0vdev0vring1>; power-domain = <0x18110005>; mboxes = <&ipi_mailbox_rpu0 0>, <&ipi_mailbox_rpu0 1>; mbox-names = "tx", "rx"; }; r5f_1 { compatible = "xilinx,r5f"; #address-cells = <0x2>; #size-cells = <0x2>; ranges; sram = <0x42 0x43>; memory-region = <&rproc_1_reserved>, <&rpu1vdev0buffer>, <&rpu1vdev0vring0>, <&rpu1vdev0vring1>; power-domain = <0x18110006>; mboxes = <&ipi_mailbox_rpu1 0>, <&ipi_mailbox_rpu1 1>; mbox-names = "tx", "rx"; }; }; zynqmp_ipi1 { compatible = "xlnx,zynqmp-ipi-mailbox"; interrupt-parent = <&gic>; interrupts = <0 33 4>; xlnx,ipi-id = <5>; #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <1>; ranges; /* APU<->RPU0 IPI mailbox controller */ ipi_mailbox_rpu0: mailbox@ff990600 { reg = <0xff3f0ac0 0x20>, <0xff3f0ae0 0x20>, <0xff3f0740 0x20>, <0xff3f0760 0x20>; reg-names = "local_request_region", "local_response_region", "remote_request_region", "remote_response_region"; #mbox-cells = <1>; xlnx,ipi-id = <3>; }; /* APU<->RPU1 IPI mailbox controller */ ipi_mailbox_rpu1: mailbox@ff990640 { reg = <0xff3f0b00 0x20>, <0xff3f0b20 0x20>, <0xff3f0940 0x20>, <0xff3f0960 0x20>; reg-names = "local_request_region", "local_response_region", "remote_request_region", "remote_response_region"; #mbox-cells = <1>; xlnx,ipi-id = <4>; }; }; }; &amba { zyxclmm_drm { compatible = "xlnx,zocl-versal"; }; };
Build the PetaLinux project and package the BOOT.bin
Code Block $ petalinux-build $ petalinux-package --boot --plm --psmfw --u-boot --dtb
Running the firmware
SD Booting
Version 2020.2
From your <plnx-proj-root>/images/linux folder, copy the BOOT.bin, image.ub and boot.scr to the SD card.
Version 2021.1
From your <plnx-proj-root>/images/linux folder, copy BOOT.BIN ,Image , boot.scr , rootfs.cpio.gz.u-boot and system.dtb to SD card
| Note |
|---|
Known issue: In 2020.x, the TTC is put in reset by the PM framework. As a workaround, you will need to request for the TTC node (PM_DEV_TTC_0 (0x18224024U)) using the SysFS interface. |
| Code Block |
|---|
echo pm_request_node 0x18224024 0x7 0x64 0 > /sys/kernel/debug/zynqmp-firmware/pm |
The list of device nodes and their respective values can be found in the Versal Software Developers Guide UG1304 here https://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/sw_manuals/xilinx2020_1/ug1304-versal-acap-ssdg.pdf#page=217
Load and start the firmware using remoteproc sysfs.
| Code Block |
|---|
echo freertos_hello_world_r50.elf > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/firmware
echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state |
Below is a snippet of the boot console.
| Code Block |
|---|
PetaLinux 2020.2 xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2 /dev/ttyAMA0
xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2 login: root
Password:
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:~# lsmod
Tainted: G
zocl 126976 0 - Live 0xffff800008c20000 (O)
zynqmp_r5_remoteproc 20480 0 - Live 0xffff800008c40000
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:~# echo stop > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state
[ 96.037285] remoteproc remoteproc0: stopped remote processor r5@0
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:~# cd /lib/firmware/
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:/lib/firmware# ls
aie freertos_hello_world_r50.elf
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:/lib/firmware# echo pm_request_node 0x18224024 0x7 0x64 0 > /sys/kernel/debug/zynqmp-firmware/pm
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:/lib/firmware# echo freertos_hello_world_r50.elf > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/firmware
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:/lib/firmware# echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state
[ 159.487837] remoteproc remoteproc0: powering up r5@0
[ 159.491488] remoteproc remoteproc0: Booting fw image freertos_hello_world_r50.elf, size 629284
[ 159.692086] remoteproc remoteproc0: header-less resource table
[ 159.693294] remoteproc remoteproc0: header-less resource table
[ 159.693643] r5@0: RPU boot from TCM.
[ 159.709198] remoteproc remoteproc0: remote processor r5@0 is now up
Hello from Freertos example main
root@xilinx-vck190-es1-2020_2:/lib/firmware# Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World
Successfully ran FreeRTOS Hello World Example
|
Booting using QEMU
In 2021.1, package the rootfs into the qemu_boot.img
| Code Block |
|---|
$ petalinux-package --boot --u-boot --qemu-rootfs images/linux/rootfs.cpio.gz.u-boot --force
$ petalinux-boot --qemu --kernel |
Snippet of qemu boot console
| Code Block |
|---|
root@xilinx-vck190-2021_1:~# lsmod Tainted: G zocl 151552 0 - Live 0xffff800008d8a000 (O) zynqmp_r5_remoteproc 16384 0 - Live 0xffff800008d80000 uio_pdrv_genirq 16384 0 - Live 0xffff800008d85000 root@xilinx-vck190-2021_1:~# cd /lib/firmware/ root@xilinx-vck190-2021_1:/lib/firmware# ls freertos_hello_world.elf root@xilinx-vck190-2021_1:/lib/firmware# echo freertos_hello_world_r50.elf > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/firmware root@xilinx-vck190-es1-20202021_21:/lib/firmware# echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state [ 159 95.487837947112] remoteproc remoteproc0: powering up r5@0ff9a0000.rf5ss:r5f_0 [ 159 95.491488953763] remoteproc remoteproc0: Booting fw image freertos_hello_world_r50.elf, size 629284913976 [ 15996.692086022718] remoteproc remoteproc0: header-less resource table [ 15996.693294023252] remoteproc remoteproc0: header-lessno resource table found. [ 159 96.693643025618] remoteproc r5@0remoteproc0: RPUheader-less bootresource fromtable TCM.[ [ 15996.709198146313] remoteproc remoteproc0: remote processor r5@0ff9a0000.rf5ss:r5f_0 is now up Hello from Freertos example main root@xilinx-vck190-es1-20202021_21:/lib/firmware# Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Rx task received string from Tx task: Hello World Successfully ran FreeRTOS Hello World Example |
...