Zynq UltraScale MPSoC Non Secure Boot
Table of Contents
1.0 Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC boot in Non Secure Boot
This page provides the instructions to create images and boot the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoc in Non-Secure method.
This page addresses the procedures based on the following
1. ZCU102 hardware platform
2. QEMU simulation platform
1.1 ZCU102 Hardware platform
This section provides the image creation and flashing procedures in Non Secure mode for ZCU102 hardware platform1. Generation of images using PetaLinux environment.
2. Programming QSPI flash from U-Boot and verify the QSPI boot.
3. Programming QSPI flash from Linux and verify the QSPI boot.
4. Programming the SD Card from Linux and verify the SD boot.
5. Booting Linux from U-Boot using TFTP.
1.1.1 Generate images using PetaLinux environment
Follow the steps below to create boot images using Petalinux on Host Linux PC
1. Set the Petalinux environment using the following command based on shell or cshell prompt
$ source <Petalinux installation path>/settings64.sh |
$ source <Petalinux installation path>/settings64.csh |
$ source <SDK installation path>/installs/lin64/SDK/<SDK release version>/settings64.sh |
$ source <SDK installation path>/installs/lin64/SDK/<SDK release version>/settings64.csh |
$ petalinux-create -t project -n <project-name> --template zynqMP $ cd <project-name> |
petalinux-config |
Figure 1: Configure the Ethernet settings as static
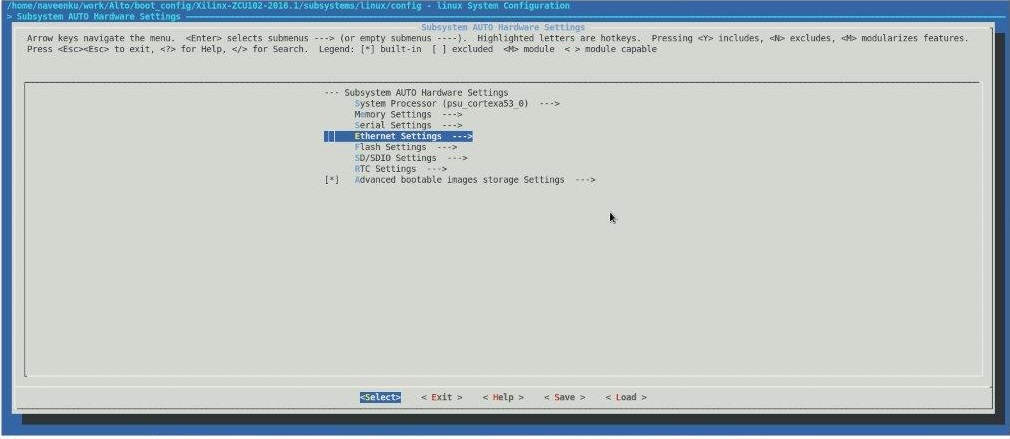
Figure 2: Configure the qspi partition information.
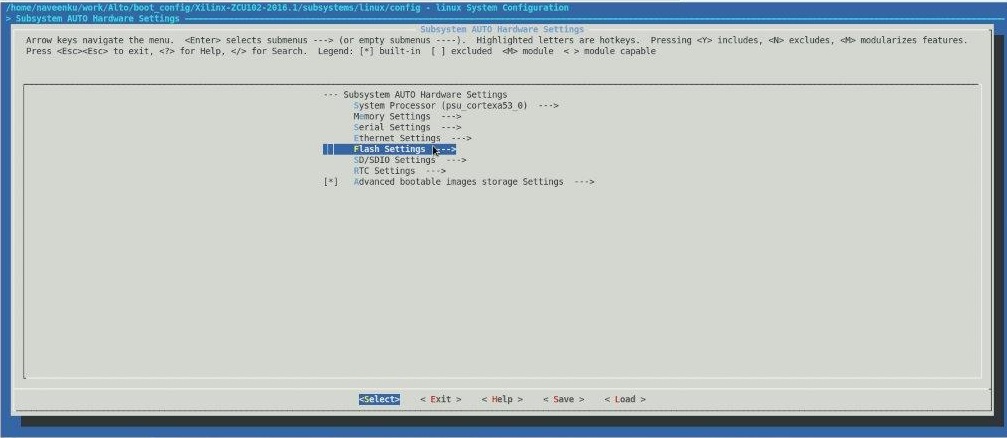
Figure 3: Set the QSPI partitions

Figure 4: Uncheck the tftp boot from Image package Configuration.

5. Modify the QSPI partitions information in device tree file system-conf.dtsi as follows
&&qspi {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
flash0: flash@0 {
compatible = "micron,n25q128";
reg = <0x0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
spi-max-frequency = <50000000>;
partition@0x00000000 {
label = "boot";
reg = <0x00000000 0x100000>;
};
partition@0x01000000 {
label = "bootenv";
reg = <0x00100000 0x40000>;
};
partition@0x00140000 {
label = "kernel";
reg = <0x00140000 0x2000000>;
};
partition@0x01240000 {
label = "device-tree";
reg = <0x02140000 0x80000>;
};
};
};
|
5. Build the images using Petalinux utils as follows
$ petalinux-build -v(verbose) |
Tested images are in
1.1.2 Programming the QSPI flash from U-Boot and verify the QSPI boot.
1. Refer to the section Generate Boot Images using Petalinux
2. Create the boota53_sd.bif for making the SD images as follows
the_ROM_image:
{
[fsbl_config] a53_x64
[bootloader] zynqmp_fsbl.elf
[destination_cpu=a53-0] bl31.elf
[destination_cpu=a53-0] u-boot.elf
} |
$ cd images/linux $ bootgen -image boota53_sd.bif -arch zynqmp -w -o i boot.bin |
the_ROM_image:
{
[fsbl_config] a53_x64
[bootloader] zynqmp_fsbl.elf
[destination_cpu=a53-0] hello_world_a53_0.elf
} |
$ cd images/linux $ bootgen -image boota53_qspi.bif -arch zynqmp -w -o i boot_qspi.bin |
7. Connect the board as per the following figure with SW6 as follows for SD card

8. Connect the Serial Cable to the board and Open the serial terminal connected on COM interface0 with settings as below figure
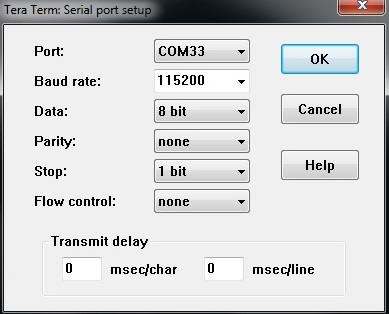
9. Power on the board, user can see the log on the serial terminal stops at u-boot prompt
10. Copy the boot_qspi.bin from SD card into QSPI using the following commands
ZynqMP>sf probe 0 0 0 ZynqMP>sf erase 0 0x100000 ZynqMP>fatload mmc 0 0x100000 boot_qspi.bin ZynqMP>sf write 0x100000 0x0 0x100000 |
12. User should see the Hello World A53_0 message on the serial terminal.
1.1.3 Programming the QSPI flash from Linux and verify the QSPI boot.
1. Refer to the section Generate Boot Images using Petalinux.
2. Create the "boota53_sd.bif" with the following contents:
$cat boot_sd.bif
the_ROM_image:
{
[fsbl_config] a53_x64
[bootloader] zynqmp_fsbl.elf
[destination_cpu=a53-0] bl31.elf
[destination_cpu=a53-0] u-boot.elf
} |
3. Create the boot.bin for SD Card using the following commands
$ cd images/linux $ bootgen -image boota53_sd.bif -arch zynqmp -w -o i boot.bin |
4. Copy the images(boot.bin, image.ub, Image and system.dtb) into SD card.
5. Insert the SD-MMC memory card on the ZCU102 board. Refer to Figure 5 For SD boot mode switch settings
6. Connect the Serial Cable to the board and Open the serial terminal connected on COM interface0. Refer to the Figure 6.
7. Power on the board. User can see the log on the serial terminal .
8. Once the Linux boots up , login ID prompts, provide login details as follows
ID : "root"
password : "root"
9. Mount the SD card using the following commands
root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: mkdir /mnt/sd root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: mount /dev/mmcblk0<p1> /mnt/sd root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: cd /mnt/sd |
10. Copy the images from SD card to QSPI MTD partition as per the MTD partitions on the board
$cat /proc/mtd
root@Xilinx-ZCU102-2016_1:/mnt/sd# cat /proc/mtd dev: size erasesize name mtd0: 00100000 00002000 "boot" mtd1: 00040000 00002000 "bootenv" mtd2: 02000000 00002000 "kernel" mtd3: 00020000 00002000 "devicetree" mtd4: 00100000 00002000 "qspi-fsbl-uboot" mtd5: 01e00000 00002000 "qspi-linux" mtd6: 00020000 00002000 "qspi-device-tree" |
root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: flashcp -v boot.bin /dev/mtd0 root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: flashcp -v Image /dev/mtd2 root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: flashcp -v system.dtb /dev/mtd3 |
11. Restart the board by keeping the boot mode in QSPI. Refer to the Figure 7
12. Stop at u-boot prompt
13. Booting from QSPI, following commands should run manually on u-boot prompt.
14. Linux should boot from QSPI flash.
1.1.4 Programming the SD Card from Linux and verify the SD boot
1. Refer to the section Generate Boot Images using PetaLinux
2. Assuming that the QSPI is already flashed using the QSPI flashing from Linux Procedure. Refer to Figure 7 for QSPI boot mode.
3. Connect the Serial Cable to the board and Open the serial terminal connected on COM interface0 with settings. Refer to Figure 6.
4. Power on the board with QSPI mode. User can see the log on the serial terminal
5. Once the Linux boots up and login ID prompts, provide the login details as below.
ID : "root"
password :"root"
6. Mount the SD card using the following commands
root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: mkdir /mnt/sd root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: mkdosfs /dev/mmcblk0 root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: mount /dev/mmcblk0 /mnt/sd root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: cd /mnt/sd |
7. Copy the image from QSPI MTD partition to SD Card. To know which corresponds to QSPI partition, use
$cat /proc/mtd
root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>:/mnt/sd# cat /proc/mtd dev: size erasesize name mtd0: 00100000 00002000 "boot" mtd1: 00040000 00002000 "bootenv" mtd2: 02000000 00002000 "kernel" mtd3: 00020000 00002000 "devicetree" mtd4: 00100000 00002000 "qspi-fsbl-uboot" mtd5: 01e00000 00002000 "qspi-linux" mtd6: 00020000 00002000 "qspi-device-tree" |
root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: cp /dev/mtd<part> boot.bin root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: cp /dev/mtd<part> Image root@Xilinx-ZCU102-<release>: cp /dev/mtd<part> system.dtb |
8. Restart the board by keeping the boot mode in SD. Refer to Figure 5 for SD boot mode.
9. User should see the Linux booting on the serial terminal using SD card.
1.1.5 Booting Linux From U-Boot Using TFTP
Procedure to be followed on the Host PC
1. Download TFTP server application from Cnet .
2. Install the application
3. Set the current directory path to the folder in which images are generated.
4. Configure the client ip address in tftp server.
Procedure to be followed on ZCU102 Target board
1.Refer to the section Generate Boot Images using Petalinux
2.Create the "boota53_sd.bif" with the following contents:
$cat boota53_sd.bif
the_ROM_image:
{
[fsbl_config] a53_x64
[bootloader] zynqmp_fsbl.elf
[destination_cpu=a53-0] bl31.elf
[destination_cpu=a53-0] u-boot.elf
} |
$ cd images/linux $ bootgen -image boota53_sd.bif -arch zynqmp -w -o i boot.bin |
5. Connect the board for SD boot mode. Refer to Figure 5.
6. Connect the board and the host PC with a Ethernet Cable.
7. Connect the Serial Cable to the board. Refer to Figure 6 for console settings
8. Power on the board. User can see the log on the serial terminal which stops at u-boot prompt
9. Set the environment to setup the server and client ip address on u-boot prompt
setenv serverip <ip-address> setenv ipaddr <ip-address> |
setenv tftpblocksize 512 |
11. Run a ping test to check if the connection is properly set.
ping <serverip>
If ping test works in U-boot, user should see the following log being displayed on the console
ZynqMP> ping 10.10.70.101 Gem.ff0e0000 Waiting for PHY auto negotiation to complete...... done Using Gem.ff0e0000 device host 10.10.70.101 is alive |
12. Run the following commands to download the kernel and the device tree images.
tftpb 0x200000 Image tftpb 0x7000000 system.dtb |
13. Run the boot command
booti 0x200000 - 0x7000000 |
14.Kernel will boot and come to the linux prompt
1.2 QEMU Prodecures
The below section describes booting of QEMU in Non-Secure mode using the following boot devices:
- QSPI24
- NAND
- SD
1.2.1 QSPI24 Non-Secure Boot
1. Set the Petalinux environment using the following command
$source <Petalinux installation path>/settings.sh
2. Create a bif file “QSPI_R5_0.bif” with the following contents:
$cat QSPI_R5_0.bif
the_ROM_image:
{
[fsbl_config] r5_single
[bootloader] R5_FSBL.elf
[destination_cpu=r5-0] R5_core0_hello_world.elf
} |
3. Run the bootgen tool to generate the bin file
$ bootgen -r -w –image ./QSPI_R5_0.bif -o Boot.bin
4. Create the QEMU QSPI single mode boot image
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=qemu_qspi_R5_0.bin bs=32M count=1
1+0 records in 1+0 records out 33554432 bytes (34 MB) copied, 0.300993 s, 111 MB/s |
87448+0 records in 87448+0 records out 87448 bytes (87 kB) copied, 3.14043 s, 27.8 kB/s |
5. Now the QEMU QSPI single mode boot image qemu_qspi_R5_0.bin can be used for the execution on QEMU
6. Execute the application on R5 core-0 using the following command
$ qemu-system-aarch64 -nographic -M arm-generic-fdt -dtb ./xilinx-zynqmp-arm.dtb -device loader,file=R5_FSBL.elf,cpu=4 -device loader,addr=0xff5e023c,
data=0x80008fde,data-len=4 -device loader,addr=0xff9a0000,data=0x80000218,data-len=4 -mtdblock qemu_qspi_R5.bin -boot mode=1
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Xilinx Resticted QEMU Sep 29 2014 20:00:35. This QEMU binary and its source are restricted to Xilinx internal use only. Do not delete this message in source. Contact the Xilinx QEMU Maintainer (git-dev@xilinx.com) for details on publishing QEMU contributions to customers. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Xilinx First Stage Boot Loader Release SW Beta1 Feb 5 2015-12:13:50 Platform: QEMU, RTL Version: 400 Cluster ID 0x80000004 Running on R5-0 Processor Processor Initialization Done In Stage 2 QSPI 24bit Boot Mode QSPI is in single flash connection Single Flash Information FlashID=0x20 0xBB 0x19 MICRON 256M Bits Multiboot Reg : 0x0 QSPI Reading Src 0x44, Dest FFFF6574, Length 4 .QSPI Reading Src 0x98, Dest FFFF6550, Length 4 .Image Header Table Offset 0x8C0 QSPI Reading Src 0x8C0, Dest FFFF1690, Length 40 .*Image Header Table Details* Boot Gen Ver: 0x1020000 No of Partitions: 0x4 Partition Header Address: 0x260 Partition Present Device: 0x0 QSPI Reading Src 0x980, Dest FFFF16D0, Length 40 .QSPI Reading Src 0x9C0, Dest FFFF1710, Length 40 .QSPI Reading Src 0xA00, Dest FFFF1750, Length 40 .QSPI Reading Src 0xA40, Dest FFFF1790, Length 40 .Initialization Success In Stage 3, Partition No:1 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x2 Data word offset: 0x2 Total Data word length: 0x2 Destination Load Address: 0x10223C Execution Address: 0x100000 Data word offset: 0x4C9E Partition Attributes: 0x508 QSPI Reading Src 0x13278, Dest 10223C, Length 8 .Partition 1 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:2 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x25 Data word offset: 0x25 Total Data word length: 0x25 Destination Load Address: 0x0 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x4CA0 Partition Attributes: 0x508 Address 0xFFE00000, Length 10000, ECC initialized QSPI Reading Src 0x13280, Dest FFE00000, Length 94 .Partition 2 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:3 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x894 Data word offset: 0x894 Total Data word length: 0x894 Destination Load Address: 0x100000 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x4CD0 Partition Attributes: 0x508 QSPI Reading Src 0x13340, Dest 100000, Length 2250 ...Partition 3 Load Success All Partitions Loaded In Stage 4 Running Cpu Handoff address: 0x100000, Exec State: 8 Exit from FSBL Hello World |
1.2.2 NAND Non-Secure Boot
1. Set the Petalinux environment using the following command
$source <Petalinux installation path>/settings.sh
2. Create a bif file “NAND.bif” with the following contents:
$cat NAND.bif
the_ROM_image:
{
[fsbl_config] a5x_x64
[bootloader] ron_a53_fsbl.elf
[destination_cpu=a5x-0] hello_world.elf
} |
$ bootgen -r -w –image ./NAND.bif -o Boot.bin
4. Create the NAND boot image
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=nand.bin bs=1G count=4
4+0 records in 4+0 records out 4294967296 bytes (4.3 GB) copied, 50.9095 s, 84.4 MB/s |
170980+0 records in 170980+0 records out 170980 bytes (171 kB) copied, 0.168898 s, 1.0 MB/s |
$ qemu-nand-creator 16384 < nand.bin > qemu_nand.bin
(87 kB) copied, 3.14043 s, 27.8 kB/s |
7. Execute the application on A53 core-0 using the following command
$ qemu-system-aarch64 -nographic -M arm-generic-fdt -hw-dtb xilinx-zynqmp-arm.dtb -device loader,file=./fsbl_a530.elf,cpu=0 -device loader,addr=0xfd1a0104,
data=0x8000000e,data-len=4 -pflash qemu_nand.bin -boot mode=4
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Xilinx Restricted QEMU Feb 13 2015 16:19:45. This QEMU binary and its source are restricted to Xilinx internal use only. Do not delete this message in source. Contact the Xilinx QEMU Maintainer (qemu-dev@xilinx.com) for details on publishing QEMU contributions to customers. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- WARNING: Image format was not specified for 'qemu_nand.bin' and probing guessed raw. Automatically detecting the format is dangerous for raw images, write operations on block 0 will be restricted. Specify the 'raw' format explicitly to remove the restrictions. DDR test pass Xilinx First Stage Boot Loader Release SW Beta1 Feb 11 2015-18:14:27 Platform: QEMU, RTL Version: 400 Cluster ID 0x80000000 Running on A53-0 Processor Processor Initialization Done In Stage 2 NAND Boot Mode Manufacturer: MICRON MT29F32G08ABCDBJ4 , Device Model: MT29F32G08ABCDBJ4 , Jedec ID: 0x2C Bytes Per Page: 0x4000 Spare Bytes Per Page: 0x4C0 Pages Per Block: 0x100 Blocks Per LUN: 0x418 Number of LUNs: 0x1 Number of bits per cell: 0x1 Number of ECC bits: 0x1 Block Size: 0x400000 Number of Target Blocks: 0x418 Number of Target Pages: 0x41800 Nand Init Success Multiboot Reg : 0x0 Image Header Table Offset 0x8C0 *Image Header Table Details* Boot Gen Ver: 0x1020000 No of Partitions: 0x5 Partition Header Address: 0x260 Partition Present Device: 0x0 Initialization Success In Stage 3, Partition No:1 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x6C8 Data word offset: 0x6C8 Total Data word length: 0x6C8 Destination Load Address: 0x0 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x7ED2 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 1 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:2 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x23A Data word offset: 0x23A Total Data word length: 0x23A Destination Load Address: 0x1B40 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x85A0 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 2 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:3 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x1F02 Data word offset: 0x1F02 Total Data word length: 0x1F02 Destination Load Address: 0x2440 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x87E0 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 3 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:4 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x9 Data word offset: 0x9 Total Data word length: 0x9 Destination Load Address: 0x1AB4 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0xA6F0 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 4 Load Success All Partitions Loaded In Stage 4 Running Cpu Handoff address: 0x0, Exec State: 0 Exit from FSBL Hello World |
1.2.3 SD Non-Secure Boot
1. Set the Petalinux environment using the following command$source <Petalinux installation path>/settings.sh
2. Create a bif file “SD.bif” with the following contents:
$ cat SD.bif
the_ROM_image:}}
{
[fsbl_config] a5x_x64
[bootloader] ron_a53_fsbl.elf
[destination_cpu=a5x-0] A53_core0_hello_world.elf
} |
$ bootgen -r -w -image SD.bif -o Boot.bin
4. Create the QEMU SD boot image
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=qemu_sd.img bs=128M count=1
1+0 records in 1+0 records out 134217728 bytes (134 MB) copied, 1.23445 s, 109 MB/s |
mkfs.fat 3.0.26 (2014-03-07 |
5. Now the QEMU SD mode boot image qemu_sd.img can be used for the execution on QEMU
6. Execute the application on R5 core-0 using the following command
$ qemu-system-aarch64 -nographic -M arm-generic-fdt -dtb ./
xilinx-zynqmp-arm.dtb
-device loader,file=ron_a53_fsbl.elf,cpu=0 -device loader,addr=0xfd1a0104,
data=0x8000000e,data-len=4 -sd qemu_sd.img -boot mode=5
---- Xilinx Resticted QEMU Sep 29 2014 20:00:35. This QEMU binary and its source are restricted to Xilinx internal use only. Do not delete this message in source. Contact the Xilinx QEMU Maintainer (git-dev@xilinx.com) for details on publishing QEMU contributions to customers. ---- Xilinx First Stage Boot Loader Release SW Beta1 Jan 29 2015-14:44:00 Platform: QEMU, RTL Version: 400 Cluster ID 0x80000000 Running on A53-0 Processor Processor Initialization Done In Stage 2 SD Boot Mode SD: rc= 0 File name is BOOT.BIN Multiboot Reg : 0x0 Image Header Table Offset 0x8C0 *Image Header Table Details* Boot Gen Ver: 0x1020000 No of Partitions: 0x5 Partition Header Address: 0x260 Partition Present Device: 0x0 Initialization Success In Stage 3, Partition No:1 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x6CE Data word offset: 0x6CE Total Data word length: 0x6CE Destination Load Address: 0x0 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x7ED2 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 1 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:2 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x23A Data word offset: 0x23A Total Data word length: 0x23A Destination Load Address: 0x1B40 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x85A0 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 2 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:3 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x1F02 Data word offset: 0x1F02 Total Data word length: 0x1F02 Destination Load Address: 0x2440 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0x87E0 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 3 Load Success In Stage 3, Partition No:4 UnEncrypted data Length: 0x9 Data word offset: 0x9 Total Data word length: 0x9 Destination Load Address: 0x1AB4 Execution Address: 0x0 Data word offset: 0xA6F0 Partition Attributes: 0x100 Partition 4 Load Success All Partitions Loaded In Stage 4 Running Cpu Handoff address: 0x0, Exec State: 0 Exit from FSBL Hello World running on A53 core 0 |
Related Links
Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC Secure BootZynq Ultrascale+ MPSoC Multiboot and Fallback