RFSoC Data Converter Evaluation Tool Getting Started Guide
The below sections describe the build and run flow tutorial.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
UI Flow
Run the RF_DC_Evaluation_UI.exe to launch the UI. The UI Launch page looks as shown in the below figure:
UI Options
In this section, we will go through the major UI menu commands and tabs
Menu
File
File|Load/Save configuration Configuration here means the settings of the RFSoC block, for example, real or I/Q mode, mixer settings, enable or bypass of internal PLL. All these settings can be saved and restored from a file on a PC.
Configuration files should be placed in \Config\ path with extension .cfg
File| Load/Save preferences Preferences is the settings of this software UI, including all the tabs that are opened, the mapping in Multi View mode, number of samples.
User can save preferred settings of UI and restore whenever is required.
Preference files should be saved in \Config\ path with extension .prf
File|Export ADC Data This command exports ADC captured data of selected ADC channels with .lvm file format. The default directory is \Data\ADC\
File|Exit Exits the software.
Edit
Standard Windows edit menu
Settings
Settings|Communication
To set your preferred communication protocol and interface.
Note: For this evaluation tool, select Ethernet interface only.
Settings|Data Folders
Choose your preferred folders for DAC test vector, saved ADC data and on board clocking frequency configuration files. By default, it is under path
\Data\ with folder name of ADC, DAC and Clocking respective.
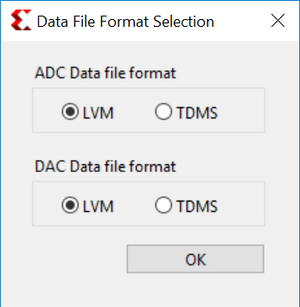
Settings|Data File Format
Choose your preferred file format between .lvm and .tdms.
Note: Sample data files for DAC are located in RFDC_UI_1.0\Data\DAC.
Window
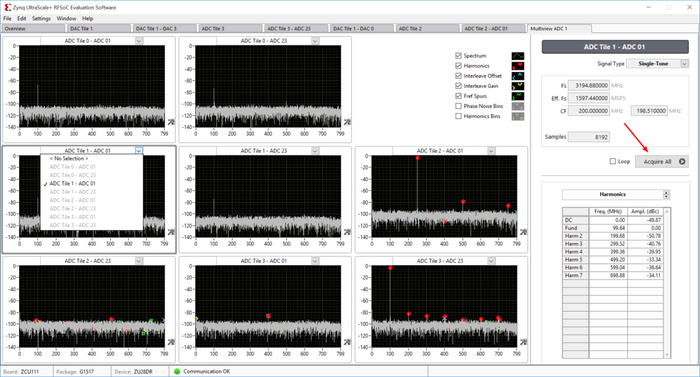
Window | MultiView
MultiView opens all the ADC or DAC FFT plots in their respective pages, with option of selecting channel for each window. Clicking on ’Acquire All’ will update all windows with respective plots.
Window|Commands log
This opens the commands log window. You can dump commands history and API response in this window.
Window|Merge all windows You can drag any opened tab to a separate window, this command will merge all separate tab to one window.
Help
Help|About About provide some general information of this Evaluation UI. You can check the version here, which might be needed when building .lvm file.
Tab
Overview
This is the home page of this UI, it shows top level framework of all converters grouped in a tile. User will see this page on UI start up.
On board Clocking, DAC output Voltage, Memory Type and Multi-Tile Sync (MTS)
In Overview tab, click Settings.It will open Onboard PLL and DAC Output Settings UI on the right panel. Evaluation UI provides the option of Predefined and Advanced mode for onboard clock setting.
In predefined mode, available frequencies are provided in a drop-down list for both ADC and DAC. The user can select a sampling frequency and then click on Apply. Evaluation UI will begin programming of onboard RFPLL.
The UI will open by default in BRAM mode. The user has an option to change the memory type between BRAM and DDR modes. Refer to Appendix B Switching between memory types types for the procedure to change memory type.
The UI supports Multi-Tile Synchronization feature which will synchronize all the DAC and ADC channels. Refer to Multi-tile Synchronization (MTS) Run Flow for the procedure to test MTS feature.
ADC/DAC Tile
In Overview tab, click any tile of ADC or DAC. This will open the individual tile page as shown below.
In this tab, you can reset, shutdown, start a tile. You can also get current tile status by clicking on the Refresh button.
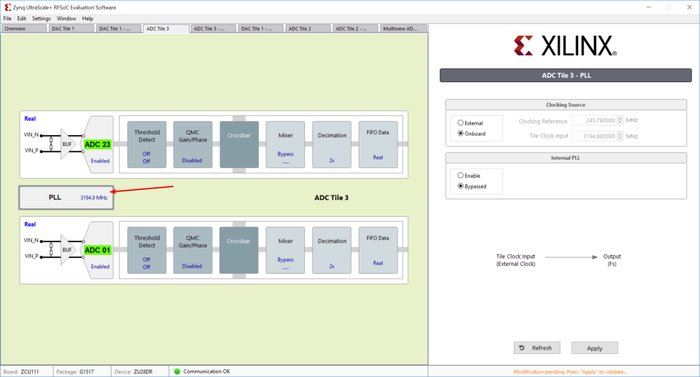
Tile PLL settings
In tile setting page, click on the PLL box, this will open the PLL settings in right panel as shown in below figure. User can choose the clock source of converter tile either from onboard PLL (LMX2594) or output of internal PLL.
For choosing external clock you need to solder a capacitor on board (refer to UG1271 for more details), feed clock through XM500 daughter card and disable related output from onboard RFPLL. Please make sure correct clock frequency is supplied from external source.
Note: 0dBm clock power is required to drive RFSoC clock input for specified performance. Insertion loss should be taken into account when clocking RFSoC directly through XM500 board. Suggested value is 1 to 7dBm from lower frequency to 6 GHz.
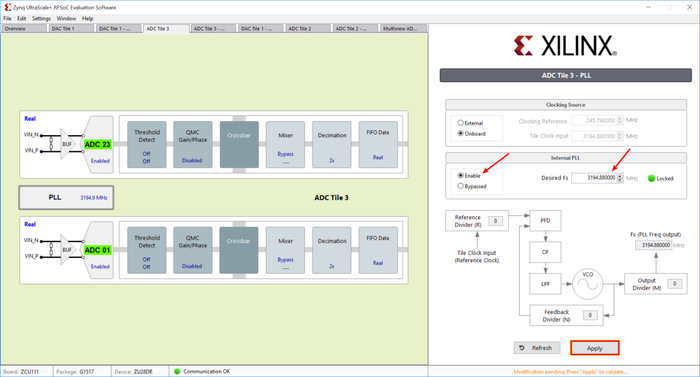
User should make sure the input clock rate is proper while using internal PLL enabled or when operating in bypass mode. When bypassing internal PLL, the input clock is sampling clock of converter, which is in general of the order of several GHz. On enabling internal PLL, the input clock is less than 1GHz. Please refer to RFSoC datasheet (DS926) for getting the proper frequencies both for using internal as well as external PLL.
Choose enable internal PLL as shown in the diagram and type the desired sampling frequency. Click on Apply.
Converter Settings
In each ADC/DAC tile, the available converter channels along with internal cascaded functional blocks are shown in block diagram. Clicking any functional block will show configuration page on the right panel. FIFO and Crossbar have their own separate pages.
ADC Settings
Calibration Mode Indicates the optimized calibration mode based on signal location in the spectrum.
Nyquist Zone Enables a user to choose which Nyquist zone the input signal should be located. This is related to interleaving calibration, should be indicated correctly. Zone 1 for odd and Zone 2 for even.
Threshold Detection Sets embedded threshold detection parameter.
Decimation Settings Allows a user to select the decimation factor. Don’t select off otherwise some digital blocks will be powered down and there won’t be any output.
DAC Settings
Decoder Mode Enables a user to select between optimized noise floor or high linearity. Noise floor optimization should be chosen for communication application.
Nyquist Zone Enables a user to choose which Nyquist zone the input signal should be located. This is related to interleaving calibration, should be indicated correctly. Zone 1 for odd and Zone 2 for even.
Interpolation Settings Allows a user to select interpolation factor. Don’t select off otherwise some digital blocks will be powered down and there won’t be any output.
Inverse Sinc Settings Enables Inverse Sinc to compensate sinc roll off at high frequency. This function is effective only when signal is in Nyquist zone 1.
Same settings in ADC and DAC
Mixer Settings Please set CrossBar page first, then set other parameters related to mixer and NCO.
QMC Settings When enabling QMC block please set the gain, phase mismatch and offset mismatch.
FIFO Data Settings Choose the number of words on AXI4S bus in PL side. Not currently supported.
FIFO This page is only for information, no configurable settings currently available.
CrossBar
Click CrossBar button at the bottom of converter settings page, or the CrossBar box in left diagram. This page determines the Real or Complex mode of Mixer and the multi-band configuration for Analog port.
FFT page
Clicking Acquisition button in ADC settings page, or Generation button in DAC settings page, will open the FFT page.
In DAC FFT page, single tone and dual tone generator is embedded in the UI. To generate complex modulated signal, user can load test vectors from a file.
There are variations of sub-menus in this page, including signal characteristics, customizing FFT plot, windowing function, test vector input and output etc. Refer to ADC FFT page as displayed below.
Note: For ADC FFT Analysis Max Hold is enabled by Default. Max Hold mode retains information of previous acquisition.
Major functions and sub-menus in FFT page.
Note: Introduction of window function will cause some performance value degradation and this will NOT be compensated in this software. Please take this in to consideration when evaluating ADC performance. For example NSD will degrade around 2dB when you introduce a window function.
Hardware and Software Design Flow
Building the RFdc Hardware Design
Refer to the Vivado Design Suite User Guide: Using the Vivado IDE, UG893, for setting up Vivado environment.
To build the hardware design, execute the following steps:
On Windows:
- Open a Vivado Tool.
- Navigate to the Eval Tool Folder Path and Change Directory to /pl folder.
- On the Tcl Console of the tool, type
source ./scripts/create_project.tcl
On Linux:
Please set $DCET_HOME environment variable as given below for linux environment
| Code Block |
|---|
% export DCET_HOME=</path/to/download/zipfile>/rdf0476-zcu111-RFdc-eval-tool-2018-3 |
1. Open a Linux terminal.
2. Change directory to $DCET_HOME/pl
3. There are three packages in the PL folder, user has to change directory accordingly.
4. To create the Vivado IPI project and invoke the UI, run the following command.
| Code Block |
|---|
% vivado -source scripts/create_project.tcl |
After executing the script on windows/linux systems, the vivado IPI block design comes up as shown in the following figure.
5. Click the "Generate Bitstream" on left hand side of Vivado Project Panel.
Note: If the user gets any pop-up with "No implementation Results available". Click "Yes". Then, if any pop-up comes up with "Launch runs", Click "OK".
The design is implemented, and a pop-up window comes up saying "Open Implemented Design". Click "OK".
Below figure depicts the view of opened implemented design.
Note: The actual results might graphically look different than the image shown.
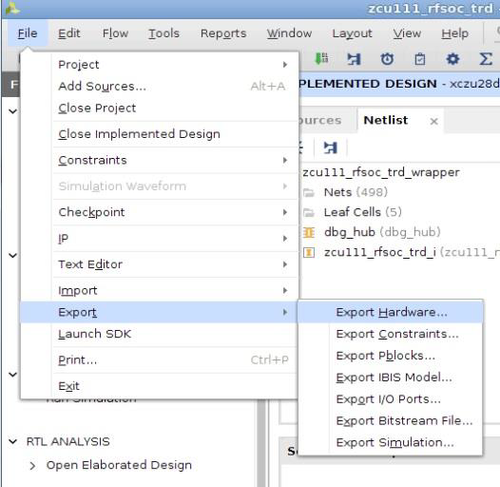
6. Go to File > Export > Export Hardware
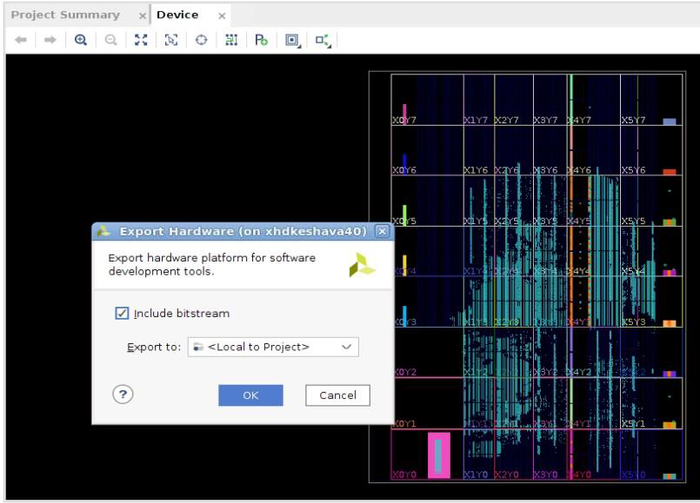
7. In the Export Hardware Platform for SDK window select "Include bitstream" and click "OK".
The XSA is created at $DCET_HOME/pl/project/zcu111_rfsoc_trd.sdk/zcu111_rfsoc_trd_wrapper.xsa
Exporting Hardware in 2020.1
- From the Vivado toolbar, select File → Export → Export Hardware.The Export Hardware dialog box opens.
- Choose Fixed and click Next.
- Choose Include device image and click Next.
- Provide the name for your exported file and choose the location. Click Next.
- A warning message appears if a Hardware Module has already been exported. Click Yes to overwrite the existing XSA file, if the overwrite message is displayed.Click Finis
Building the PetaLinux Project
...
.jpg?version=1&modificationDate=1545044455635&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=400)